The secure encryption of data, which prevents access and manipulation by unauthorized persons, is a central requirement for many digital applications - whenever sensitive, confidential and sensitive information is involved. This ranges from online banking to the exchange of secret data between state institutions.
There are a number of methods that can be used to encode data in such a sophisticated way that even supercomputers cannot decode them in a reasonable amount of time. This is generally considered safe.
However, some of the encryption methods commonly used today will probably no longer be secure in the foreseeable future. Namely when quantum computers are able to break these codes. Nobody can say with certainty whether and when the performance of quantum computers will be sufficient for this. But theoretically they have this power and, according to experts, it seems to be only a matter of time before the technology of these exotic computers will be ready.
It is therefore advisable to prepare for the era of quantum computers today and to develop alternative encryption methods that can also withstand the attack of a quantum computer.
One way is to strike back with the weapons of quantum physics and use them for rock-solid encryption. The so-called quantum encryption uses the entanglement of light particles. A pioneer of this technology is the Viennese physicist Anton Zeilinger, who was the first to transmit encrypted data using entangled light particles, initially in the laboratory, then also through kilometers of glass fibers and finally also wirelessly through the air.
Zeilinger successfully conducted the first experiment back in 1999. Five years later, his research team exchanged entangled photons via a 600-meter-long fiber optic cable between Vienna City Hall and a bank branch.
In 2012, entangled photons were transmitted over a distance of 143 kilometers from the Canary Island of La Palma to neighboring Tenerife. Zeilinger was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2022 for this groundbreaking work.
So far, the Chinese have been in the lead in the practical application of this technology. In 2017, they launched a quantum satellite that enables tap-proof communication between several base stations.
In Europe, the importance of quantum communication has also been recognized. The European Union is now funding the QUDICE project with 4.3 million euros, in which space-compatible hardware for highly secure quantum communication via satellites is to be developed.
At the heart of this is a miniaturized source for entangled photons, which is said to be only about the size of a tetrapak milk carton. It will be developed by an international team of researchers over the next three years. Institutes and companies in Italy, Spain, France, Malta and Germany are involved. In Germany, it is scientists at the Fraunhofer Institute for Applied Optics and Precision Engineering in Jena.
The common goal is the development of a photon source that provides one billion entangled light particles per second. This enables a correspondingly high bit rate. According to the researchers, the current state of the art is several orders of magnitude below the target rate.
The new hardware should one day become the basis for a European satellite network with which data can be exchanged securely. The first step towards developing a highly secure pan-European infrastructure for more data security was taken in 2019 with an agreement between the EU Commission and the European Space Agency Esa.

 What is chloropicrin, the chemical agent that Washington accuses Moscow of using in Ukraine?
What is chloropicrin, the chemical agent that Washington accuses Moscow of using in Ukraine? Poland, big winner of European enlargement
Poland, big winner of European enlargement In Israel, step-by-step negotiations for a ceasefire in the Gaza Strip
In Israel, step-by-step negotiations for a ceasefire in the Gaza Strip BBVA ADRs fall almost 2% on Wall Street
BBVA ADRs fall almost 2% on Wall Street Sánchez cancels his agenda and considers resigning: "I need to stop and reflect"
Sánchez cancels his agenda and considers resigning: "I need to stop and reflect" The Federal Committee of the PSOE interrupts the event to take to the streets with the militants
The Federal Committee of the PSOE interrupts the event to take to the streets with the militants Repsol: "We want to lead generative AI to guarantee its benefits and avoid risks"
Repsol: "We want to lead generative AI to guarantee its benefits and avoid risks" Osteoarthritis: an innovation to improve its management
Osteoarthritis: an innovation to improve its management The yen jumps 3% then falls again, amid speculation of Japanese intervention
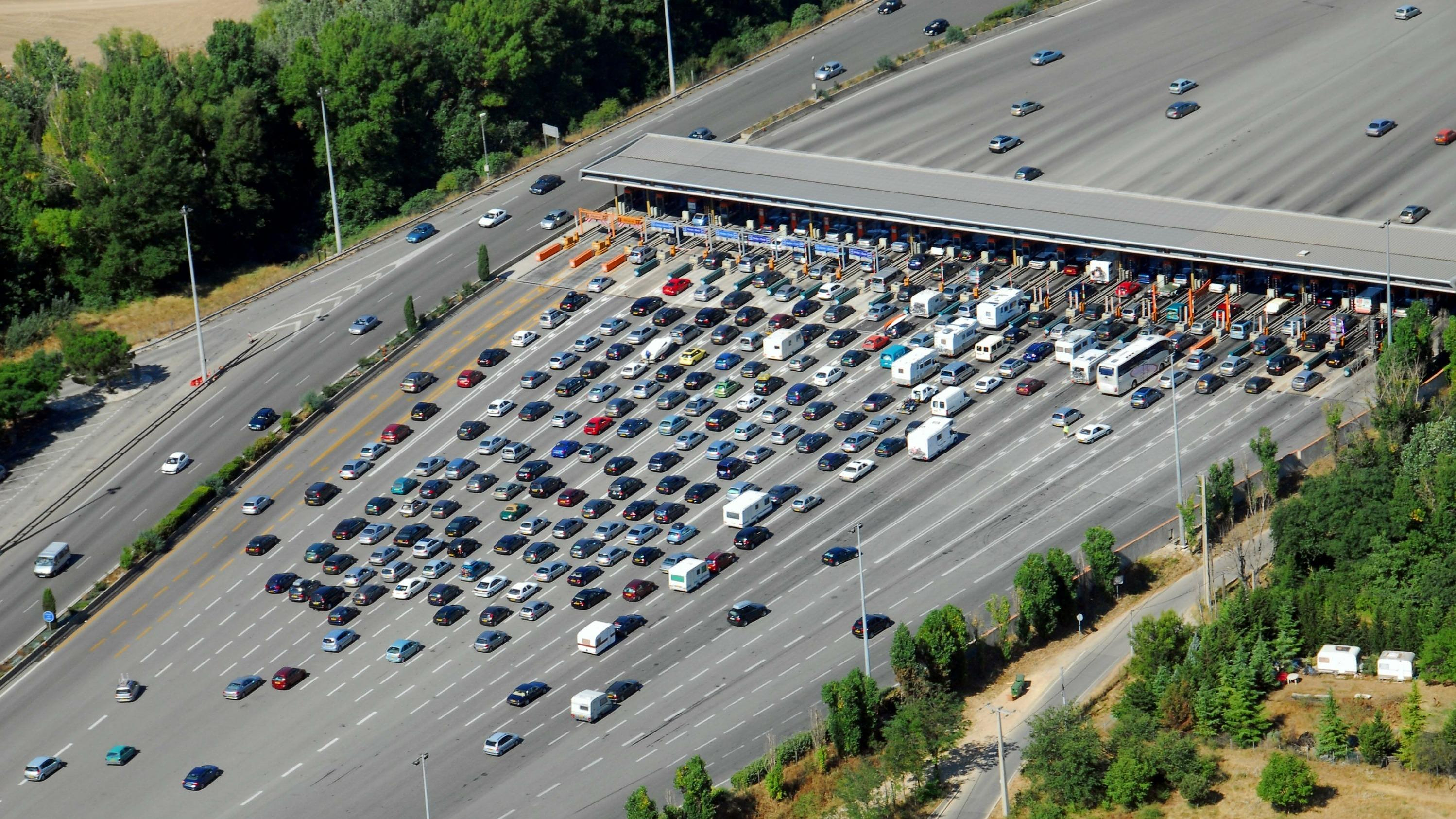
The yen jumps 3% then falls again, amid speculation of Japanese intervention A very busy Friday on the roads of Île-de-France before the Ascension Bridge
A very busy Friday on the roads of Île-de-France before the Ascension Bridge Fraud: the government is preparing new measures for the fall
Fraud: the government is preparing new measures for the fall Nike breaks the bank to keep the Blues jersey
Nike breaks the bank to keep the Blues jersey Madonna ends her world tour with a giant - and free - concert in Copacabana
Madonna ends her world tour with a giant - and free - concert in Copacabana Harry Potter: Daniel Radcliffe “really saddened” by his final breakup with J.K. Rowling
Harry Potter: Daniel Radcliffe “really saddened” by his final breakup with J.K. Rowling Leviathan, New York Trilogy... Five books by Paul Auster that you must have read
Leviathan, New York Trilogy... Five books by Paul Auster that you must have read Italy wins a decisive round against an American museum for the restitution of an ancient bronze
Italy wins a decisive round against an American museum for the restitution of an ancient bronze Omoda 7, another Chinese car that could be manufactured in Spain
Omoda 7, another Chinese car that could be manufactured in Spain BYD chooses CA Auto Bank as financial partner in Spain
BYD chooses CA Auto Bank as financial partner in Spain Tesla and Baidu sign key agreement to boost development of autonomous driving
Tesla and Baidu sign key agreement to boost development of autonomous driving Skoda Kodiaq 2024: a 'beast' plug-in hybrid SUV
Skoda Kodiaq 2024: a 'beast' plug-in hybrid SUV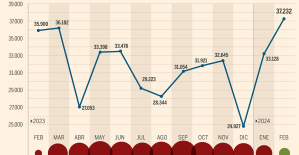 The home mortgage firm rises 3.8% in February and the average interest moderates to 3.33%
The home mortgage firm rises 3.8% in February and the average interest moderates to 3.33%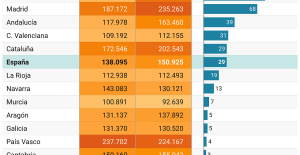 This is how housing prices have changed in Spain in the last decade
This is how housing prices have changed in Spain in the last decade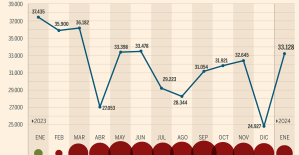 The home mortgage firm drops 10% in January and interest soars to 3.46%
The home mortgage firm drops 10% in January and interest soars to 3.46% The jewel of the Rocío de Nagüeles urbanization: a dream villa in Marbella
The jewel of the Rocío de Nagüeles urbanization: a dream villa in Marbella Europeans: a senior official on the National Rally list
Europeans: a senior official on the National Rally list Blockade of Sciences Po: the right denounces a “drift”, the government charges the rebels
Blockade of Sciences Po: the right denounces a “drift”, the government charges the rebels Even on a mission for NATO, the Charles-de-Gaulle remains under French control, Lecornu responds to Mélenchon
Even on a mission for NATO, the Charles-de-Gaulle remains under French control, Lecornu responds to Mélenchon “Deadly Europe”, “economic decline”, immigration… What to remember from Emmanuel Macron’s speech at the Sorbonne
“Deadly Europe”, “economic decline”, immigration… What to remember from Emmanuel Macron’s speech at the Sorbonne These French cities that will boycott the World Cup in Qatar
These French cities that will boycott the World Cup in Qatar Mercato: Verratti at Barça? A track studied
Mercato: Verratti at Barça? A track studied Rugby: after the defeat during the Six Nations, the Blues will meet the English in September for a test match
Rugby: after the defeat during the Six Nations, the Blues will meet the English in September for a test match Premier League: Liverpool unveils its new jersey for next season
Premier League: Liverpool unveils its new jersey for next season Formula 1: Alpine holds its new executive technical director
Formula 1: Alpine holds its new executive technical director