Rare familial Form of Alzheimer's disease: disease-triggering changes occur mainly in three genes: the App Gene, in the Presenilin1 Gene (most common), in the Presenilin2 Gene (the most rare). All the three genes found mutations increase the production and deposition of Beta-Amyloid in the brain of the Affected.
Common sporadic Form of Alzheimer's disease: The gene variant APOE 4 is one of the biggest risk factors for Alzheimer's disease if it occurs twice, so one copy from the father and from the mother is inherited. More than 40 percent of people with Alzheimer's disease have two copies of APOE 4.
another Gene, a variant of TREM 2, presents an equally high risk of Contracting Alzheimer's disease like APOE 4. TREM 2 plays an important role in the Microglia, the phagocytes of the brain.
Also protective gene mutations are known. The APOE3/Christchurch-mutant of the Colombian woman is the new. It was known that the variant APOE2 protects in duplicate. In the Icelandic population, as well as in Finland, Norway and Sweden, researchers found a rare genetic mutation. It relates to the APP-gen thanks to this change, the makers produce less Beta-Amyloid. (afo)
Created: 07.11.2019, 20:31 PM

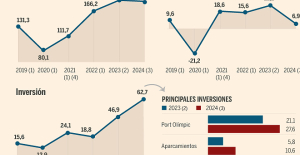 B:SM will break its investment record this year with 62 million euros
B:SM will break its investment record this year with 62 million euros War in Ukraine: when kyiv attacks Russia with inflatable balloons loaded with explosives
War in Ukraine: when kyiv attacks Russia with inflatable balloons loaded with explosives United States: divided on the question of presidential immunity, the Supreme Court offers respite to Trump
United States: divided on the question of presidential immunity, the Supreme Court offers respite to Trump Maurizio Molinari: “the Scurati affair, a European injury”
Maurizio Molinari: “the Scurati affair, a European injury” First three cases of “native” cholera confirmed in Mayotte
First three cases of “native” cholera confirmed in Mayotte Meningitis: compulsory vaccination for babies will be extended in 2025
Meningitis: compulsory vaccination for babies will be extended in 2025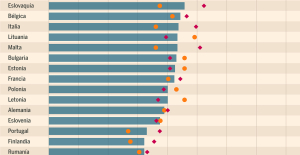 Spain is the country in the European Union with the most overqualified workers for their jobs
Spain is the country in the European Union with the most overqualified workers for their jobs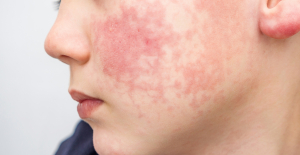 Parvovirus alert, the “fifth disease” of children which has already caused the death of five babies in 2024
Parvovirus alert, the “fifth disease” of children which has already caused the death of five babies in 2024 Inflation rebounds in March in the United States, a few days before the Fed meeting
Inflation rebounds in March in the United States, a few days before the Fed meeting Video games: Blizzard cancels Blizzcon 2024, its annual high mass
Video games: Blizzard cancels Blizzcon 2024, its annual high mass Falling wings of the Moulin Rouge: who will pay for the repairs?
Falling wings of the Moulin Rouge: who will pay for the repairs? “You don’t sell a company like that”: Roland Lescure “annoyed” by the prospect of a sale of Biogaran
“You don’t sell a company like that”: Roland Lescure “annoyed” by the prospect of a sale of Biogaran Exhibition: in Deauville, Zao Wou-Ki, beauty in all things
Exhibition: in Deauville, Zao Wou-Ki, beauty in all things Dak’art, the most important biennial of African art, postponed due to lack of funding
Dak’art, the most important biennial of African art, postponed due to lack of funding In Deadpool and Wolverine, Ryan and Hugh Jackman explore the depths of the Marvel multiverse
In Deadpool and Wolverine, Ryan and Hugh Jackman explore the depths of the Marvel multiverse Tom Cruise returns to Paris for the filming of Mission Impossible 8
Tom Cruise returns to Paris for the filming of Mission Impossible 8 Skoda Kodiaq 2024: a 'beast' plug-in hybrid SUV
Skoda Kodiaq 2024: a 'beast' plug-in hybrid SUV Tesla launches a new Model Y with 600 km of autonomy at a "more accessible price"
Tesla launches a new Model Y with 600 km of autonomy at a "more accessible price" The 10 best-selling cars in March 2024 in Spain: sales fall due to Easter
The 10 best-selling cars in March 2024 in Spain: sales fall due to Easter A private jet company buys more than 100 flying cars
A private jet company buys more than 100 flying cars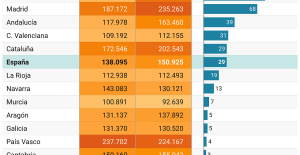 This is how housing prices have changed in Spain in the last decade
This is how housing prices have changed in Spain in the last decade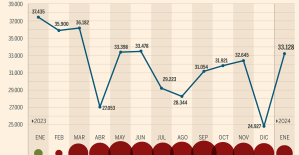 The home mortgage firm drops 10% in January and interest soars to 3.46%
The home mortgage firm drops 10% in January and interest soars to 3.46% The jewel of the Rocío de Nagüeles urbanization: a dream villa in Marbella
The jewel of the Rocío de Nagüeles urbanization: a dream villa in Marbella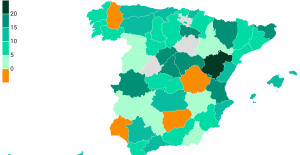 Rental prices grow by 7.3% in February: where does it go up and where does it go down?
Rental prices grow by 7.3% in February: where does it go up and where does it go down? Even on a mission for NATO, the Charles-de-Gaulle remains under French control, Lecornu responds to Mélenchon
Even on a mission for NATO, the Charles-de-Gaulle remains under French control, Lecornu responds to Mélenchon “Deadly Europe”, “economic decline”, immigration… What to remember from Emmanuel Macron’s speech at the Sorbonne
“Deadly Europe”, “economic decline”, immigration… What to remember from Emmanuel Macron’s speech at the Sorbonne Sale of Biogaran: The Republicans write to Emmanuel Macron
Sale of Biogaran: The Republicans write to Emmanuel Macron Europeans: “All those who claim that we don’t need Europe are liars”, criticizes Bayrou
Europeans: “All those who claim that we don’t need Europe are liars”, criticizes Bayrou These French cities that will boycott the World Cup in Qatar
These French cities that will boycott the World Cup in Qatar Euroleague: at the end of the suspense, Monaco equalizes against Fenerbahçe
Euroleague: at the end of the suspense, Monaco equalizes against Fenerbahçe Women's Six Nations: Where to see and five things to know about France-England
Women's Six Nations: Where to see and five things to know about France-England Liverpool: it is confirmed, Slot will succeed Klopp on the Reds bench
Liverpool: it is confirmed, Slot will succeed Klopp on the Reds bench Ligue 1: Montpellier and Nantes back to back, two reds in stoppage time
Ligue 1: Montpellier and Nantes back to back, two reds in stoppage time