Christopher Schrader is a freelance writer in the science Department of the süddeutsche Zeitung. He mainly writes about energy and climate topics in Geosciences, and engineering. Schrader is Nannen physicist and a graduate of the Henri school, the school of journalism of the publishing house Gruner+Jahr. He was editor of the SZ, Geo-Knowledge and the Swiss news magazine Facts.
< p > E-Mailmosquitoes are the Empire, the most evil human killer of the animal. The blood-sucking insects transmit viruses and other pathogens: Dengue, Chikungunya, Zika, West Nile Virus, yellow fever, and Malaria. Climate change has now begun a large Migration of mosquitoes you find in many new regions with good living conditions. In Karlsruhe and other places in southern Germany, for example, experts have already been found in mosquitoes in 2017 and 2018, the Asian tigers, which were probably introduced from the South of the Alps.
climate change is likely these and other Stechtieren roll out in the coming decades in many regions of the world, so to speak, a red carpet. According to a new projection of almost a billion people could be more than in the past the tropics exposed to diseases that are transmitted by the species Aedes albopictus (tiger mosquito) and Aedes aegypti (yellow fever mosquito). The scientists led by Sadie Ryan of the University of Florida reports in Gainesville.
"people are very good at moving critters and their Pathogens across the globe," says Ryan. The researchers consider different cases: on the one Hand, to the years 2050 and 2080, on the other hand, four from the IPCC-designed scenarios, and how bad global warming is, from the maximum braked climate change in the scenario RCP2.6, that adheres to the Paris targets, and the Two-degree limit safely, to the complete unmitigated scenario RCP8.5.
Tiger and yellow fever mosquitoes in 30 years in Germany, home of the tigers to be
Thus, mosquitoes in 30 years in virtually all of Germany in the summer of one to three months for a home, even under the maximum braking climate scenarios. Yellow can keep mosquitoes fever, however, only in the North-East and South-West, mainly in Brandenburg and Baden-Württemberg, about a month long. Even such a short time present a hazard, warn the scientists, both species can breed explosively, and then an acute outbreak of a disease trigger. The temperatures should rise stronger than in the best conceivable case, the mosquitoes also better conditions. In the worst case, the insect spread nearly half of each year, their pathogen cargo.
Anyway, Europe (divided into West, middle and East) at the top of the hit list of the regions which could have the most of the new victims: depending on the scenario and time period is 150 to 470 million in the case of the yellow fever, and 230 to 440 million in the case of the tiger mosquito. Just East Africa the yellow fever mosquito is also one of the first three places in the growth statistics. There is then in the same order of magnitude as in Central Europe 50 million to 90 million potentially re-infecting people.
Should run the climate change unabated, practically, then it is likely to be for the tiger in some regions of the world already too hot for mosquitoes. You not only tolerate good 29 degrees Celsius, then the transfer of disease works agents as well. The result is that in RCP8.5 in large Parts of South-East Asia, Africa and in the Amazon basin the rates of infection by Aedes albopictus fall. The one should not hold but for good news, warns Colin Carlson of Georgetown University in Washington DC: "Every scenario in which it will be too hot for the transmission of the Dengue pathogen, contains other and similar to dangerous changes in the health sector."

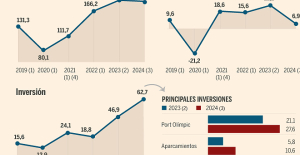 B:SM will break its investment record this year with 62 million euros
B:SM will break its investment record this year with 62 million euros War in Ukraine: when kyiv attacks Russia with inflatable balloons loaded with explosives
War in Ukraine: when kyiv attacks Russia with inflatable balloons loaded with explosives United States: divided on the question of presidential immunity, the Supreme Court offers respite to Trump
United States: divided on the question of presidential immunity, the Supreme Court offers respite to Trump Maurizio Molinari: “the Scurati affair, a European injury”
Maurizio Molinari: “the Scurati affair, a European injury” First three cases of “native” cholera confirmed in Mayotte
First three cases of “native” cholera confirmed in Mayotte Meningitis: compulsory vaccination for babies will be extended in 2025
Meningitis: compulsory vaccination for babies will be extended in 2025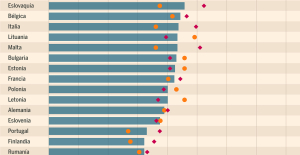 Spain is the country in the European Union with the most overqualified workers for their jobs
Spain is the country in the European Union with the most overqualified workers for their jobs Parvovirus alert, the “fifth disease” of children which has already caused the death of five babies in 2024
Parvovirus alert, the “fifth disease” of children which has already caused the death of five babies in 2024 Inflation rebounds in March in the United States, a few days before the Fed meeting
Inflation rebounds in March in the United States, a few days before the Fed meeting Video games: Blizzard cancels Blizzcon 2024, its annual high mass
Video games: Blizzard cancels Blizzcon 2024, its annual high mass Falling wings of the Moulin Rouge: who will pay for the repairs?
Falling wings of the Moulin Rouge: who will pay for the repairs? “You don’t sell a company like that”: Roland Lescure “annoyed” by the prospect of a sale of Biogaran
“You don’t sell a company like that”: Roland Lescure “annoyed” by the prospect of a sale of Biogaran Exhibition: in Deauville, Zao Wou-Ki, beauty in all things
Exhibition: in Deauville, Zao Wou-Ki, beauty in all things Dak’art, the most important biennial of African art, postponed due to lack of funding
Dak’art, the most important biennial of African art, postponed due to lack of funding In Deadpool and Wolverine, Ryan and Hugh Jackman explore the depths of the Marvel multiverse
In Deadpool and Wolverine, Ryan and Hugh Jackman explore the depths of the Marvel multiverse Tom Cruise returns to Paris for the filming of Mission Impossible 8
Tom Cruise returns to Paris for the filming of Mission Impossible 8 Skoda Kodiaq 2024: a 'beast' plug-in hybrid SUV
Skoda Kodiaq 2024: a 'beast' plug-in hybrid SUV Tesla launches a new Model Y with 600 km of autonomy at a "more accessible price"
Tesla launches a new Model Y with 600 km of autonomy at a "more accessible price" The 10 best-selling cars in March 2024 in Spain: sales fall due to Easter
The 10 best-selling cars in March 2024 in Spain: sales fall due to Easter A private jet company buys more than 100 flying cars
A private jet company buys more than 100 flying cars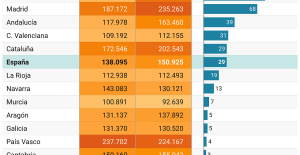 This is how housing prices have changed in Spain in the last decade
This is how housing prices have changed in Spain in the last decade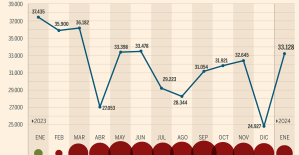 The home mortgage firm drops 10% in January and interest soars to 3.46%
The home mortgage firm drops 10% in January and interest soars to 3.46% The jewel of the Rocío de Nagüeles urbanization: a dream villa in Marbella
The jewel of the Rocío de Nagüeles urbanization: a dream villa in Marbella Rental prices grow by 7.3% in February: where does it go up and where does it go down?
Rental prices grow by 7.3% in February: where does it go up and where does it go down? Even on a mission for NATO, the Charles-de-Gaulle remains under French control, Lecornu responds to Mélenchon
Even on a mission for NATO, the Charles-de-Gaulle remains under French control, Lecornu responds to Mélenchon “Deadly Europe”, “economic decline”, immigration… What to remember from Emmanuel Macron’s speech at the Sorbonne
“Deadly Europe”, “economic decline”, immigration… What to remember from Emmanuel Macron’s speech at the Sorbonne Sale of Biogaran: The Republicans write to Emmanuel Macron
Sale of Biogaran: The Republicans write to Emmanuel Macron Europeans: “All those who claim that we don’t need Europe are liars”, criticizes Bayrou
Europeans: “All those who claim that we don’t need Europe are liars”, criticizes Bayrou These French cities that will boycott the World Cup in Qatar
These French cities that will boycott the World Cup in Qatar Euroleague: at the end of the suspense, Monaco equalizes against Fenerbahçe
Euroleague: at the end of the suspense, Monaco equalizes against Fenerbahçe Women's Six Nations: Where to see and five things to know about France-England
Women's Six Nations: Where to see and five things to know about France-England Liverpool: it is confirmed, Slot will succeed Klopp on the Reds bench
Liverpool: it is confirmed, Slot will succeed Klopp on the Reds bench Ligue 1: Montpellier and Nantes back to back, two reds in stoppage time
Ligue 1: Montpellier and Nantes back to back, two reds in stoppage time