the Projections can ”sometimes have scientific causes as the background, but for the most part the information should be taken as curiosities.”
So writes the Swedish meteorological and hydrological institute, on its website if the predictions of the Swedish bondepraktika. Fog in march the learn portend rain at midsummer. If Josefdagen is clear and beautiful does it mean that it will be a fruitful odlingsår.
Even the financial markets has its mainstreaming manual with the wisdoms, predictions and various prognosregler. One such is the ”interest rate curve”. The show right now crop.
the short explanation. Under normal circumstances, the variable interest rates lower than the interest rate on long-term loans. So it is when households lend to the dwelling. So it wont be when the state gives out government bonds. All who want to bind their interest to pay a premium. It is called that the interest rate curve slightly upwards.
But sometimes it happens that the premium falls, the relationship flips and the short-term loans become more expensive than long. You are talking about an inverted interest rate curve. It is not a good sign. Since the second world war, it has never – with the occasional exception, gone wrong. When the u.s. interest rate curve is turned over ends up in the US economy soon in recession.
On 22 march of this year, it happened again. The interest rate on ten-year us treasuries are now lower than tremånadersräntan. It is an omen that set the horror in the financial markets.
there Are sure signs that there will be a recession?
Link to the graphics
Several studies suggest that the interest rate curve actually manage to predict the economic cycle with some years of advance planning. In a long flashback that was conducted in 2008 concluded that the interest rate curve was a better krisvarnare than the professional forecasters.
But the measure is not infallible. Research shows that the accuracy has weakened in recent decades. A possible explanation is that the central banks – which control short-term interest rates – have become better at catching up on the warning signs and push away declines in time.
the Links, however, varies over time and between countries. It seems that the united states is a special case. In Europe and Sweden has the interest rate curve historically have been less reliable. In Japan, where the policy rate has been extremely low for a long period, it is probably better to trace in the tea leaves. Räntekurvans prophetic power is, therefore, no universal law.
A hefty decline on the stock exchange usually do not both good. A decline reflects pessimism, and in addition, falling share values reinforce a sense of both households and businesses that they are becoming poorer. It makes them extra cautious.
the market goes, therefore, to use as a very rough forecast of how the economy will develop. But the courses swing too much. The economist Paul Samuelson said in the 1960s that the stock market managed to predict nine of the last five recessionerna. It has been shown to be quite close to the truth. The stock exchange is an alarmist.
Many difficult economic downturns throughout history have struck in the context of a financial crisis, which, in turn, preceded by a kreditrally with growing debts and rising prices of real estate and shares.
the Pattern is well known. A new study from the Bank of International Settlements, the central banks ' central bank, has also identified some useful measures of risk.
An indicator that is highlighted is the firms 'and households' total interest payments and repayments of principal. When this debt burden rises and reaches a peak increases the risk of a recession within two years, shows the study. The authors claim that their indicator is just a bit better than the interest rate curve.
the Official economic statistics and the established barometers are the sources of private forecasters and public policy-makers usually prefer when they look to the future.
the National institute of economic measures, the Swedish household and corporate expectations in the regular surveys. How do they look at the future? What are they planning to buy? Swedbank also has a private purchasing managers ' index, which measures the mood in the service sector and industry.
Such konjunkturmått often provide reliable information. The downside is that they rarely manage to predict the hearty downs before they are a fact. Economic crises are generally not, therefore, in the conventional forecasts. The national financial management authority director-general, Clas Olsson called it recently, ”forecasters ' cowardice”.
on the question of whether you can certainly know when the recession will are inclined, therefore, to a no.
the Economy changes. The old equilibria exception can be made, new kraftspel makes itself suddenly felt. And the surest prophesies of events far into the future should – unfortunately – be taken as occult curiosities rather than science.

 War in Ukraine: when kyiv attacks Russia with inflatable balloons loaded with explosives
War in Ukraine: when kyiv attacks Russia with inflatable balloons loaded with explosives United States: divided on the question of presidential immunity, the Supreme Court offers respite to Trump
United States: divided on the question of presidential immunity, the Supreme Court offers respite to Trump Maurizio Molinari: “the Scurati affair, a European injury”
Maurizio Molinari: “the Scurati affair, a European injury” Hamas-Israel war: US begins construction of pier in Gaza
Hamas-Israel war: US begins construction of pier in Gaza First three cases of “native” cholera confirmed in Mayotte
First three cases of “native” cholera confirmed in Mayotte Meningitis: compulsory vaccination for babies will be extended in 2025
Meningitis: compulsory vaccination for babies will be extended in 2025 Spain is the country in the European Union with the most overqualified workers for their jobs
Spain is the country in the European Union with the most overqualified workers for their jobs Parvovirus alert, the “fifth disease” of children which has already caused the death of five babies in 2024
Parvovirus alert, the “fifth disease” of children which has already caused the death of five babies in 2024 Inflation rebounds in March in the United States, a few days before the Fed meeting
Inflation rebounds in March in the United States, a few days before the Fed meeting Video games: Blizzard cancels Blizzcon 2024, its annual high mass
Video games: Blizzard cancels Blizzcon 2024, its annual high mass Falling wings of the Moulin Rouge: who will pay for the repairs?
Falling wings of the Moulin Rouge: who will pay for the repairs? “You don’t sell a company like that”: Roland Lescure “annoyed” by the prospect of a sale of Biogaran
“You don’t sell a company like that”: Roland Lescure “annoyed” by the prospect of a sale of Biogaran Exhibition: in Deauville, Zao Wou-Ki, beauty in all things
Exhibition: in Deauville, Zao Wou-Ki, beauty in all things Dak’art, the most important biennial of African art, postponed due to lack of funding
Dak’art, the most important biennial of African art, postponed due to lack of funding In Deadpool and Wolverine, Ryan and Hugh Jackman explore the depths of the Marvel multiverse
In Deadpool and Wolverine, Ryan and Hugh Jackman explore the depths of the Marvel multiverse Tom Cruise returns to Paris for the filming of Mission Impossible 8
Tom Cruise returns to Paris for the filming of Mission Impossible 8 Skoda Kodiaq 2024: a 'beast' plug-in hybrid SUV
Skoda Kodiaq 2024: a 'beast' plug-in hybrid SUV Tesla launches a new Model Y with 600 km of autonomy at a "more accessible price"
Tesla launches a new Model Y with 600 km of autonomy at a "more accessible price" The 10 best-selling cars in March 2024 in Spain: sales fall due to Easter
The 10 best-selling cars in March 2024 in Spain: sales fall due to Easter A private jet company buys more than 100 flying cars
A private jet company buys more than 100 flying cars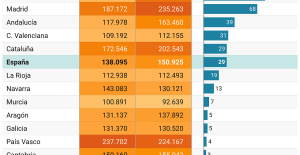 This is how housing prices have changed in Spain in the last decade
This is how housing prices have changed in Spain in the last decade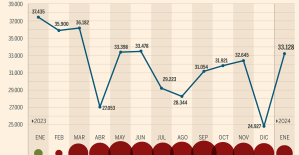 The home mortgage firm drops 10% in January and interest soars to 3.46%
The home mortgage firm drops 10% in January and interest soars to 3.46% The jewel of the Rocío de Nagüeles urbanization: a dream villa in Marbella
The jewel of the Rocío de Nagüeles urbanization: a dream villa in Marbella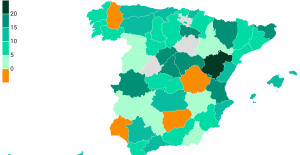 Rental prices grow by 7.3% in February: where does it go up and where does it go down?
Rental prices grow by 7.3% in February: where does it go up and where does it go down? Even on a mission for NATO, the Charles-de-Gaulle remains under French control, Lecornu responds to Mélenchon
Even on a mission for NATO, the Charles-de-Gaulle remains under French control, Lecornu responds to Mélenchon “Deadly Europe”, “economic decline”, immigration… What to remember from Emmanuel Macron’s speech at the Sorbonne
“Deadly Europe”, “economic decline”, immigration… What to remember from Emmanuel Macron’s speech at the Sorbonne Sale of Biogaran: The Republicans write to Emmanuel Macron
Sale of Biogaran: The Republicans write to Emmanuel Macron Europeans: “All those who claim that we don’t need Europe are liars”, criticizes Bayrou
Europeans: “All those who claim that we don’t need Europe are liars”, criticizes Bayrou These French cities that will boycott the World Cup in Qatar
These French cities that will boycott the World Cup in Qatar Basketball: Strasbourg appeals the victory recovered by Monaco
Basketball: Strasbourg appeals the victory recovered by Monaco Top 14: UBB with Tatafu and Moefana against Bayonne
Top 14: UBB with Tatafu and Moefana against Bayonne MotoGP: Bagnaia dominates qualifying practice in Spain and sets track record
MotoGP: Bagnaia dominates qualifying practice in Spain and sets track record Olympic Games: in Athens, Greece transmits the Olympic flame to France
Olympic Games: in Athens, Greece transmits the Olympic flame to France