The protection of Wages, allow the EU and its member States, more than Switzerland, said Luca Visentini, head of the European trade Union Confederation, in an Interview. An evaluation of the measures of the individual countries shows that the differences in the wage protection measures between the States are indeed great. A final evaluation and a comparison with Switzerland are, however, difficult.
The EU since 2014, the so-called enforcement Directive, which instruments the member States, the wage protection towards the Sending companies and their employees can control. So you may not require, for example, that the sending establishments to inform the local authorities before taking up employment in the host country. EU directives must be transposed into national law, which leaves member States a certain leeway.
The EU member States can introduce additional measures of protection. Laid down in the Directive expressly so. However, you must be "proportionate".
This formulation is also found in additional Protocol 1 of the framework agreement. Here is the proposal from the EU for the future protection of Wages in Switzerland. It provides for the Adoption of the EU posting of workers law by the Switzerland – specifically, the posting of workers Directive, in 2020, a more stringent Version in force, and the enforcement Directive.
conflicts because of the enforcement Directive
Until the summer of 2016, all EU member States had to transfer the enforcement Directive in their national legislation. Say: to determine how to use the new instruments in the protection of Wages. All member States have transposed the new Directive, says EU Commission spokesman Christian Wigand. The administration is now reviewing whether the national measures are in accordance with the Directive. For a forecast it is still too early. The EU Commission wants to publish its report in June.
There, where the member States have not transposed the enforcement Directive correctly, want Brussels to initiate infringement proceedings, the EU Commission in 2017, announced in a reply to a parliamentary question. The request of the German MEP Andreas Schwab (CDU) shows that there are between EU States is quite conflicts due to the enforcement Directive.
Schwab wanted to know from the Commission whether she was actually aware of the fact that individual member have been adopted by States "illegal" wage protection measures. The business-friendly politicians from Baden-Württemberg focused mainly on France. The country wanted in the meantime collect a flat rate fee of 40 Euro for each posted workers .
Four working - instead of eight calendar days
The chambers of industry and Commerce of the German state have an Overview of the requirements of the sending establishments in all EU-States created, and is continuously updated. It shows, among other things, that the offer of the EU to Switzerland is great especially quickly. The EU, Switzerland, to a prior notification period of four working days for posting in certain high-risk sectors to keep. Today is the deadline in Switzerland is eight calendar days.
The majority of EU States require only a notification immediately before the Start of the order. Romania knows a period of five days, Slovenia is one of the three. In France and Italy, for example, this message will, in turn, requires all the companies. In Germany, only companies from the "black work affine branches". The Czech Republic followed a reverse approach: the Czech Client has to report the posting.
contact persons in the host country
The enforcement Directive also contains accompanying measures which go further than what Switzerland does today. However, secondments of up to a year and a half are possible in the EU, while in Switzerland, only 90 days are allowed. So there is in the EU, for example, the obligation to appoint a local contact person for the authorities of the host state, sent in required documents and to make and receive notifications. In Switzerland the indication of a contact person is also provided. As the state writes Secretariat for the economy, but a less far-reaching function as the contact person of the enforcement Directive, in accordance with.
Also, these measures will be implemented in the individual EU member States in very different ways. Some forgo some other request, such as Switzerland, merely the naming of a contact person. And then, France is: Here not only the most accurate information must be provided to the representatives. This must agree to the appointment in writing and the precise details of the place, where he kept the documents to the sending order of its clients. A Pro-forma appointment of a local representative is not working.
(editing Tamedia)
Created: 07.03.2019, 19:27 PM

 Hamas-Israel war: US begins construction of pier in Gaza
Hamas-Israel war: US begins construction of pier in Gaza Israel prepares to attack Rafah
Israel prepares to attack Rafah Indifference in European capitals, after Emmanuel Macron's speech at the Sorbonne
Indifference in European capitals, after Emmanuel Macron's speech at the Sorbonne Spain: what is Manos Limpias, the pseudo-union which denounced the wife of Pedro Sánchez?
Spain: what is Manos Limpias, the pseudo-union which denounced the wife of Pedro Sánchez?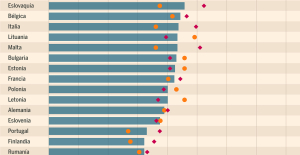 Spain is the country in the European Union with the most overqualified workers for their jobs
Spain is the country in the European Union with the most overqualified workers for their jobs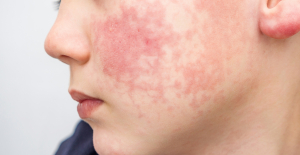 Parvovirus alert, the “fifth disease” of children which has already caused the death of five babies in 2024
Parvovirus alert, the “fifth disease” of children which has already caused the death of five babies in 2024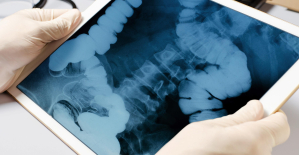 Colorectal cancer: what to watch out for in those under 50
Colorectal cancer: what to watch out for in those under 50 H5N1 virus: traces detected in pasteurized milk in the United States
H5N1 virus: traces detected in pasteurized milk in the United States Private clinics announce a strike with “total suspension” of their activities, including emergencies, from June 3 to 5
Private clinics announce a strike with “total suspension” of their activities, including emergencies, from June 3 to 5 The Lagardère group wants to accentuate “synergies” with Vivendi, its new owner
The Lagardère group wants to accentuate “synergies” with Vivendi, its new owner The iconic tennis video game “Top Spin” returns after 13 years of absence
The iconic tennis video game “Top Spin” returns after 13 years of absence Three Stellantis automobile factories shut down due to supplier strike
Three Stellantis automobile factories shut down due to supplier strike A pre-Roman necropolis discovered in Italy during archaeological excavations
A pre-Roman necropolis discovered in Italy during archaeological excavations Searches in Guadeloupe for an investigation into the memorial dedicated to the history of slavery
Searches in Guadeloupe for an investigation into the memorial dedicated to the history of slavery Aya Nakamura in Olympic form a few hours before the Flames ceremony
Aya Nakamura in Olympic form a few hours before the Flames ceremony Psychiatrist Raphaël Gaillard elected to the French Academy
Psychiatrist Raphaël Gaillard elected to the French Academy Skoda Kodiaq 2024: a 'beast' plug-in hybrid SUV
Skoda Kodiaq 2024: a 'beast' plug-in hybrid SUV Tesla launches a new Model Y with 600 km of autonomy at a "more accessible price"
Tesla launches a new Model Y with 600 km of autonomy at a "more accessible price" The 10 best-selling cars in March 2024 in Spain: sales fall due to Easter
The 10 best-selling cars in March 2024 in Spain: sales fall due to Easter A private jet company buys more than 100 flying cars
A private jet company buys more than 100 flying cars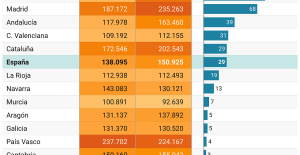 This is how housing prices have changed in Spain in the last decade
This is how housing prices have changed in Spain in the last decade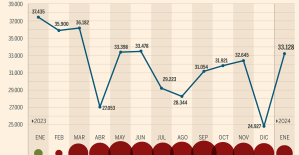 The home mortgage firm drops 10% in January and interest soars to 3.46%
The home mortgage firm drops 10% in January and interest soars to 3.46% The jewel of the Rocío de Nagüeles urbanization: a dream villa in Marbella
The jewel of the Rocío de Nagüeles urbanization: a dream villa in Marbella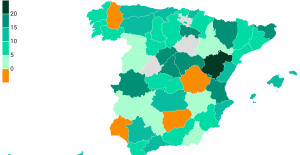 Rental prices grow by 7.3% in February: where does it go up and where does it go down?
Rental prices grow by 7.3% in February: where does it go up and where does it go down? “Deadly Europe”, “economic decline”, immigration… What to remember from Emmanuel Macron’s speech at the Sorbonne
“Deadly Europe”, “economic decline”, immigration… What to remember from Emmanuel Macron’s speech at the Sorbonne Sale of Biogaran: The Republicans write to Emmanuel Macron
Sale of Biogaran: The Republicans write to Emmanuel Macron Europeans: “All those who claim that we don’t need Europe are liars”, criticizes Bayrou
Europeans: “All those who claim that we don’t need Europe are liars”, criticizes Bayrou With the promise of a “real burst of authority”, Gabriel Attal provokes the ire of the opposition
With the promise of a “real burst of authority”, Gabriel Attal provokes the ire of the opposition These French cities that will boycott the World Cup in Qatar
These French cities that will boycott the World Cup in Qatar Judo: Blandine Pont European vice-champion
Judo: Blandine Pont European vice-champion Swimming: World Anti-Doping Agency appoints independent prosecutor in Chinese doping case
Swimming: World Anti-Doping Agency appoints independent prosecutor in Chinese doping case Water polo: everything you need to know about this sport
Water polo: everything you need to know about this sport Judo: Cédric Revol on the 3rd step of the European podium
Judo: Cédric Revol on the 3rd step of the European podium


















