Born in the 1970s, video games have continued to grow in popularity. In 2022, there would be more than 3 billion players worldwide. With the growing importance of screens, children are exposed to them at younger and younger ages. And not necessarily for their own good: if video games are known to stimulate learning or creativity, they are also factors of dependence, social isolation, and can harm vision.
On the other hand, the issue of hearing problems has often been neglected. However, during long sessions with headphones or earphones stuck to their ears, “gamers” expose themselves without realizing it to sound volumes that sometimes exceed the recommended thresholds. This behavior is increasingly alarming specialists, who point to games as an avoidable source of hearing loss. And there is no shortage of scientific evidence. A study published in BMJ Public Health examined 14 reports involving more than 50,000 players from 9 countries which demonstrate these harmful effects.
Also read: “Yes, the consequences of young people’s addiction to video games are terrible”
Some of these surveys focused on specific categories of “noisy” computer games, others on arcades (large gaming centers popular in Asia in particular), or even on smartphone games. Overall, the results are not good: “gamers” have a greater risk of partial deafness as a result of their practice. Generally more fond of video games, boys would be more concerned because they play for longer durations and at higher listening volumes than girls.
These hearing problems are variable and can become permanent. One of the most common concerns the loss of sensitivity to certain sounds. “This results in a reduced perception of the weakest sounds, such as whispers, or even high-frequency high-pitched sounds, such as “sss” or “fff”, describes Paul Avan, director of the research and development center. innovation in human audiology (CERIAH) at the Pasteur Institute. Several studies in this large analysis have also established a direct link with the development of tinnitus which can manifest itself transiently, disappearing after a moment of rest, but which sometimes sets in irreversibly.
Less frequently, exposure to sounds that are too loud causes the degradation of structures that are not directly responsible for hearing sensitivity but for the interpretation of sounds. “This problem affects the nerve fibers responsible for transmitting auditory messages to the brain. As a result, the nervous system can no longer “understand” certain perceived sounds, which impairs the understanding of a conversation, particularly in a noisy environment,” explains Professor Avan.
Generally speaking, the risk is greater when the exposure is at high volumes. For several hours a day, the hearing organs store repeated sound trauma. “The hair cells responsible for sound perception are capable of self-regeneration in the event of small traumas, but if they add up over a prolonged period, they do not have time to repair themselves and their loss becomes irreversible,” underlines Dr Laurent Tavernier, director of the ENT department at Besançon University Hospital.
Also readVideo games: what are their real effects on health?
According to WHO recommendations, adults can safely listen to sound volumes of 80 decibels (dB) for 40 hours a week, compared to 75 dB for children. This “permissible” exposure time halves for every 3 dB increase. For example, adults should not be exposed to 83 dB for more than 20 hours per week, to 86 dB for more than 10 hours and so on. The same principle applies to children (83 dB for about 6.5 hours maximum, then 86 dB for 3.35 hours, etc.). “In absolute terms, we estimate that the limits are around 100 dB for children and 120 dB for adults,” explains Dr. Tavernier. However, this tolerable limit also depends on the sensitivity of each person.
It also appears that certain categories of games expose people to louder sounds than others and are therefore more dangerous for hearing health. The sound levels evaluated by the various studies ranged from 43.2 dB for games on mobile devices, 80 to 89 dB for arcades, and even beyond 100 dB for certain computer games. A study published in 2019 notably estimated that fans of first-person shooter (FPS) games, such as Call of Duty or Battlefield, were exposed to sounds between 88.5 and 91.2 dB. Burst noises that simulate weapons (sound pulses lasting less than 1 second) could reach up to 119 dB, well beyond the threshold limit recommended for children. Also on the podium for the noisiest games were certain car racing games (85.6 dB).
Although players have the option to lower the volume, they do not do so systematically because they do not know the risk and, in practice, it is impossible to assess an exposure threshold. Specialists therefore recall the importance of raising awareness among young people and their parents. “Not to mention,” adds Professor Avan, “that games are not the only daily source of noise: add listening time in transport, in nightclubs (>102 dB), in stadiums (>105 dB) but also the screeching of the metro for example which easily exceeds 85 decibels..."
In addition to lowering the volume, taking regular breaks remains crucial to rest the ears. For serious gamers, it may also be worth investing in a gaming headset with active noise reduction. “Then it is the responsibility of the authorities and game creators to include for example daily counters which could indicate in the form of an alert if the daily sound level has been exceeded or by permanently displaying in the corner of the “color-coded screen with the sound intensity level, red if exceeded,” suggests Dr. Tavernier.

 War in Ukraine: without Russia, Crimea will become “one of the best places to live in Europe”, assures Zelensky
War in Ukraine: without Russia, Crimea will become “one of the best places to live in Europe”, assures Zelensky British justice: traditional wigs, deemed “discriminatory” by black lawyers, about to be abandoned
British justice: traditional wigs, deemed “discriminatory” by black lawyers, about to be abandoned Israel: for the first time, Eden Golan sings in public the original version of her song rejected during Eurovision
Israel: for the first time, Eden Golan sings in public the original version of her song rejected during Eurovision “Teachers are there to teach facts to students”: in the United Kingdom, the government wants to backtrack on gender theory in schools
“Teachers are there to teach facts to students”: in the United Kingdom, the government wants to backtrack on gender theory in schools Cancer: Klineo, a platform allowing patients to access new therapies
Cancer: Klineo, a platform allowing patients to access new therapies Suicide attempts and self-harm on the rise among young girls
Suicide attempts and self-harm on the rise among young girls In Europe, 10,000 people die every day from cardiovascular disease
In Europe, 10,000 people die every day from cardiovascular disease Brussels raises Spanish GDP forecasts to 2.1% and foresees a deficit of 3% in 2024
Brussels raises Spanish GDP forecasts to 2.1% and foresees a deficit of 3% in 2024 Microsoft integrates generative AI directly into its PCs
Microsoft integrates generative AI directly into its PCs “Toxic culture” at the FDIC: criticized, the boss of the American banking regulator resigns
“Toxic culture” at the FDIC: criticized, the boss of the American banking regulator resigns Donald Trump's media group lost $327 million in the first quarter
Donald Trump's media group lost $327 million in the first quarter Suspicions of favoritism: EDF and its former CEO Henri Proglio judged from this Tuesday
Suspicions of favoritism: EDF and its former CEO Henri Proglio judged from this Tuesday Theater: with Terrasses, written by Laurent Gaudé, drama and tears
Theater: with Terrasses, written by Laurent Gaudé, drama and tears Dave celebrates his 80th birthday at the Grand Rex
Dave celebrates his 80th birthday at the Grand Rex Kevin Costner's tears after the Cannes screening of his western “Horizon: an American saga”
Kevin Costner's tears after the Cannes screening of his western “Horizon: an American saga” On Broadway, George Clooney brings Good Night, and Good Luck back to life
On Broadway, George Clooney brings Good Night, and Good Luck back to life Omoda 7, another Chinese car that could be manufactured in Spain
Omoda 7, another Chinese car that could be manufactured in Spain BYD chooses CA Auto Bank as financial partner in Spain
BYD chooses CA Auto Bank as financial partner in Spain Tesla and Baidu sign key agreement to boost development of autonomous driving
Tesla and Baidu sign key agreement to boost development of autonomous driving Skoda Kodiaq 2024: a 'beast' plug-in hybrid SUV
Skoda Kodiaq 2024: a 'beast' plug-in hybrid SUV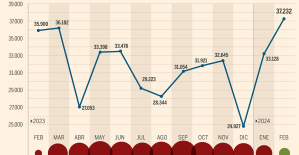 The home mortgage firm rises 3.8% in February and the average interest moderates to 3.33%
The home mortgage firm rises 3.8% in February and the average interest moderates to 3.33%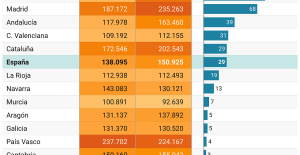 This is how housing prices have changed in Spain in the last decade
This is how housing prices have changed in Spain in the last decade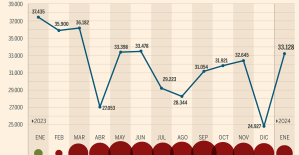 The home mortgage firm drops 10% in January and interest soars to 3.46%
The home mortgage firm drops 10% in January and interest soars to 3.46% The jewel of the Rocío de Nagüeles urbanization: a dream villa in Marbella
The jewel of the Rocío de Nagüeles urbanization: a dream villa in Marbella “Such a dear friend on whom I could always count”: the political class pays tribute to the former mayor of Marseille, Jean-Claude Gaudin
“Such a dear friend on whom I could always count”: the political class pays tribute to the former mayor of Marseille, Jean-Claude Gaudin New Caledonia: Valls pleads for a “global agreement”, Knafo judges that “France must stick to its positions”
New Caledonia: Valls pleads for a “global agreement”, Knafo judges that “France must stick to its positions” New Caledonia: Braun-Pivet wants a postponement of the Congress
New Caledonia: Braun-Pivet wants a postponement of the Congress Europeans: a “Free Palestine” list, whose logo advocates the disappearance of Israel, officially a candidate
Europeans: a “Free Palestine” list, whose logo advocates the disappearance of Israel, officially a candidate These French cities that will boycott the World Cup in Qatar
These French cities that will boycott the World Cup in Qatar Basketball: Bourg-en-Bresse brushes aside Nanterre to join Monaco in the semi-finals
Basketball: Bourg-en-Bresse brushes aside Nanterre to join Monaco in the semi-finals Giro: a special weather protocol for this Tuesday
Giro: a special weather protocol for this Tuesday Serie A: Bologna and Juventus back to back in a crazy match
Serie A: Bologna and Juventus back to back in a crazy match Tennis: Cornet and Parry fall at the start in Strasbourg
Tennis: Cornet and Parry fall at the start in Strasbourg

















