From where did the dog get its name? Scientists have discovered that humans domesticated the wolf (Canis lupus) at least 15,000 years ago during the Ice Age. However, they don't know if this happened once or multiple times. A team of archaeologists and geneticists from around the world has published in Nature that dogs (Canis familiaris) are descended from at least two distinct populations of wolves. It is possible that domestication took place in eastern Eurasia.
Anders Bergstrom from the Francis Crick Institute's Laboratory for Ancient Genomics and his collaborators have analysed 72 wolf genomes. These are those that were found in Europe, Siberia, and the Americas over the past 100,000 years. These correspond to animals that were recovered from 16 countries by archaeologists. The oldest are from Eastern Siberia, while the latest come from Europe and North America.
Six genomes, all Siberian, have been published. Nine laboratories have sequenced 66 genomes for this research. An excellently preserved Siberian Wolf head dating back 32,000 years ago was analyzed. A two-month-old Siberian cub, known as Dogor ('friend’ in Yakut), whose DNA cannot be determined if it is a wolf.
Dogor, a 2-month-old puppy that lived 18,000 years ago. / Sergei Fedorov
Researchers found that modern and primitive dogs have genetic similarities to ancient wolves from Asia, which suggests domestication in eastern Eurasia. Researchers also discovered evidence that dogs descend from two populations wolves. One oriental origin is what appears to be the source of the first dogs from Siberia, America, and northeastern Europe. The Near Eastern wolves are also evident in the descendants of the dogs that lived in the Near East, Africa and South Europe.
Bergstrom says that the dogs he discovered came from two distinct wolf populations. One was an eastern source which produced all dogs, and one that produced some dogs. The authors suggest that there are two possibilities for this dual origin. Either the wolf was domesticated multiple time and the resulting dog population mixed or the wolf was domesticated once and primitive dogs were mixed with wolves later.
Researchers have been able see how the DNA of wolves has changed over the years, as the 72 wolf genomes cover approximately 30,000 generations. Researchers have seen that a genetic variant on chromosome 25, which was once very rare, became common in all wolves. It is now found in all wolves. It affects the gene responsible for the development of the jaw and skull bones. Although the authors think that this variant was spread by an increase in prey availability during the Ice Age, it could have given wolves with certain head shapes an advantage. However, they warn that there may be other functions to the gene.
Pontus Skoglund, a researcher at the Francis Crick Institute's Ancient Genomics Laboratory, said that this is the first time scientists have followed natural selection in large animals over a 100,000 year time span. This allows them to see evolution unfold in real-time rather than trying reconstruct it from current DNA. Researchers believe that all mutations in wolves were spread quickly because of "the species being extremely connected across great distances." This connectivity may be one reason that wolves survived the Ice Age, while large carnivores like large carnivores vanished.

 United States: divided on the question of presidential immunity, the Supreme Court offers respite to Trump
United States: divided on the question of presidential immunity, the Supreme Court offers respite to Trump Maurizio Molinari: “the Scurati affair, a European injury”
Maurizio Molinari: “the Scurati affair, a European injury” Hamas-Israel war: US begins construction of pier in Gaza
Hamas-Israel war: US begins construction of pier in Gaza Israel prepares to attack Rafah
Israel prepares to attack Rafah First three cases of “native” cholera confirmed in Mayotte
First three cases of “native” cholera confirmed in Mayotte Meningitis: compulsory vaccination for babies will be extended in 2025
Meningitis: compulsory vaccination for babies will be extended in 2025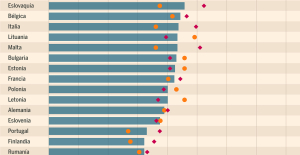 Spain is the country in the European Union with the most overqualified workers for their jobs
Spain is the country in the European Union with the most overqualified workers for their jobs Parvovirus alert, the “fifth disease” of children which has already caused the death of five babies in 2024
Parvovirus alert, the “fifth disease” of children which has already caused the death of five babies in 2024 Falling wings of the Moulin Rouge: who will pay for the repairs?
Falling wings of the Moulin Rouge: who will pay for the repairs? “You don’t sell a company like that”: Roland Lescure “annoyed” by the prospect of a sale of Biogaran
“You don’t sell a company like that”: Roland Lescure “annoyed” by the prospect of a sale of Biogaran Insults, threats of suicide, violence... Attacks by France Travail agents will continue to soar in 2023
Insults, threats of suicide, violence... Attacks by France Travail agents will continue to soar in 2023 TotalEnergies boss plans primary listing in New York
TotalEnergies boss plans primary listing in New York La Pléiade arrives... in Pléiade
La Pléiade arrives... in Pléiade In Japan, an animation studio bets on its creators suffering from autism spectrum disorders
In Japan, an animation studio bets on its creators suffering from autism spectrum disorders Terry Gilliam, hero of the Annecy Festival, with Vice-Versa 2 and Garfield
Terry Gilliam, hero of the Annecy Festival, with Vice-Versa 2 and Garfield François Hollande, Stéphane Bern and Amélie Nothomb, heroes of one evening on the beach of the Cannes Film Festival
François Hollande, Stéphane Bern and Amélie Nothomb, heroes of one evening on the beach of the Cannes Film Festival Skoda Kodiaq 2024: a 'beast' plug-in hybrid SUV
Skoda Kodiaq 2024: a 'beast' plug-in hybrid SUV Tesla launches a new Model Y with 600 km of autonomy at a "more accessible price"
Tesla launches a new Model Y with 600 km of autonomy at a "more accessible price" The 10 best-selling cars in March 2024 in Spain: sales fall due to Easter
The 10 best-selling cars in March 2024 in Spain: sales fall due to Easter A private jet company buys more than 100 flying cars
A private jet company buys more than 100 flying cars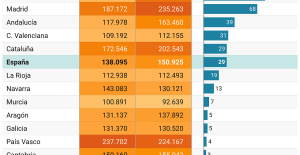 This is how housing prices have changed in Spain in the last decade
This is how housing prices have changed in Spain in the last decade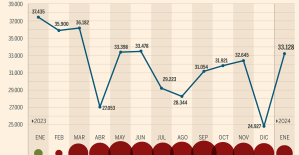 The home mortgage firm drops 10% in January and interest soars to 3.46%
The home mortgage firm drops 10% in January and interest soars to 3.46% The jewel of the Rocío de Nagüeles urbanization: a dream villa in Marbella
The jewel of the Rocío de Nagüeles urbanization: a dream villa in Marbella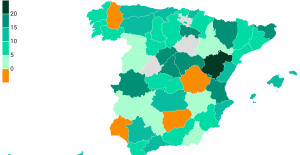 Rental prices grow by 7.3% in February: where does it go up and where does it go down?
Rental prices grow by 7.3% in February: where does it go up and where does it go down? Even on a mission for NATO, the Charles-de-Gaulle remains under French control, Lecornu responds to Mélenchon
Even on a mission for NATO, the Charles-de-Gaulle remains under French control, Lecornu responds to Mélenchon “Deadly Europe”, “economic decline”, immigration… What to remember from Emmanuel Macron’s speech at the Sorbonne
“Deadly Europe”, “economic decline”, immigration… What to remember from Emmanuel Macron’s speech at the Sorbonne Sale of Biogaran: The Republicans write to Emmanuel Macron
Sale of Biogaran: The Republicans write to Emmanuel Macron Europeans: “All those who claim that we don’t need Europe are liars”, criticizes Bayrou
Europeans: “All those who claim that we don’t need Europe are liars”, criticizes Bayrou These French cities that will boycott the World Cup in Qatar
These French cities that will boycott the World Cup in Qatar Medicine, family of athletes, New Zealand…, discovering Manae Feleu, the captain of the Bleues
Medicine, family of athletes, New Zealand…, discovering Manae Feleu, the captain of the Bleues Football: OM wants to extend Leonardo Balerdi
Football: OM wants to extend Leonardo Balerdi Six Nations F: France-England shatters the attendance record for women’s rugby in France
Six Nations F: France-England shatters the attendance record for women’s rugby in France Judo: eliminated in the 2nd round of the European Championships, Alpha Djalo in full doubt
Judo: eliminated in the 2nd round of the European Championships, Alpha Djalo in full doubt