Planning, financing, and executing a marketing campaign has the potential to be somewhat wasteful unless you take the time necessary to gauge its success (or lack thereof) with the appropriate marketing metrics. Take a superficial glance at the marketing metrics available to business owners and marketers and you’ll find there are plenty to choose from. Below, we highlight the most important marketing metrics that help determine the success of a marketing campaign.
1. Customer Lifetime Value
Customer lifetime value is a metric commonly used to quantify the financial value of a customer. If the money you spend to acquire the average customer (customer acquisition cost) exceeds that of the customer lifetime value, you are spending too much on marketing. The customer lifetime value metric tabulates the value of the customer from the initial point of contact all the way through to the last purchase made.
Use the CLV metric to get a sense of value across advertising channels, pinpoint the specific channels that have a comparably high CLV, and continue to invest in those avenues.
2. Return on Advertising Spend
Also referred to as ROAS, return on advertising spend is a tool that gauges the money made through advertising efforts. This marketing metric gauges marketing campaign performance, measuring the level of revenue obtained through advertising dollars spent, and highlighting performance on specific marketing networks. Use ROAS in the context of analyzing connected TV advertising statistics and you’ll better understand how to maximize ad performance.
3. Cost Per Thousand Impressions
The CPM, or cost per thousand impressions, is a commonly used marketing metric. CPM is the cost for every 1,000 web-based views. CPMs give you a sense of how much your ads cost per view to evaluate the financial efficacy of exposure and make necessary alterations.
4. Cost Per Lead
The cost per lead (CPL) metric is determined by dividing the money spent on a marketing push by the aggregate number of leads it yields. Cost per lead determines if a company’s current leads are generated at a rate that has the potential to prove sustainable and cost-efficient over time. CPL also empowers businesses to zero in on ways to optimize sales funnel stages to decrease cost per lead while simultaneously boosting conversions.
5. Brand Sentiment
The perception of your brand is partially dictated by your marketing campaigns. Get a sense of your brand sentiment through Google alerts that make you aware of instances when your brand name or other relevant information is mentioned in media. Develop a response plan of action to manage your brand sentiment in accordance with mentions, continue tracking mentions and it won’t take long to improve customer perception of your company.
6. ROI (Return on Investment)
Above all, ROI is the most important marketing metric. ROI is the return on marketing investment. ROI determines whether the money spent on a specific ad campaign is worthwhile. Monitor the ROI of each individual marketing campaign, make strategic alterations, and recalculate the ROI after those adjustments and it won’t take long for your bottom line to benefit.
7. Click-through rate
The click-through rate, or CTR for short, gauges the number of times an ad is clicked. This important metric reveals the online visitor’s action in the aftermath of exposure to an ad. CTR empowers business owners, managers, and marketers to obtain a better understanding of the behaviors of the target audience, helping to improve the on-site shopping experience.
8. Customer Acquisition Cost
The amount of money necessary to acquire a customer is just as important as the amount of money the average customer spends. Quantify the CAC, short for customer acquisition cost, and you’ll understand exactly what it costs to bring a prospect into the fold as a paying customer. CAC is determined by dividing the money spent on marketing by the number of acquired customers.
9. New Visitors Vs. Returning Visitors
Compare the number of new visitors to the number of returning visitors and you’ll get a sense as to whether your current marketing campaigns are driving new traffic to your site or if most of your business stems from those who previously demonstrated interest.
This metric ultimately reveals the “stickiness” of the site in the context of whether its content and marketing encourages customers to return and also whether marketing campaigns are successful in attracting new interest.
10. Return on Marketing Investment (RoMI)
RoMI is calculated by measuring marketing campaign revenue generation and comparing it to the overarching cost of operating the campaign. RoMI can be calculated with end-to-end suites and other specialized software. RoMI is useful in that it helps business owners and marketers develop a comprehensive understanding of marketing campaign performance, especially in the context of how such campaigns play a part in overarching organizational growth.

 United States: divided on the question of presidential immunity, the Supreme Court offers respite to Trump
United States: divided on the question of presidential immunity, the Supreme Court offers respite to Trump Maurizio Molinari: “the Scurati affair, a European injury”
Maurizio Molinari: “the Scurati affair, a European injury” Hamas-Israel war: US begins construction of pier in Gaza
Hamas-Israel war: US begins construction of pier in Gaza Israel prepares to attack Rafah
Israel prepares to attack Rafah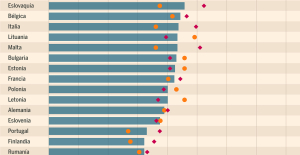 Spain is the country in the European Union with the most overqualified workers for their jobs
Spain is the country in the European Union with the most overqualified workers for their jobs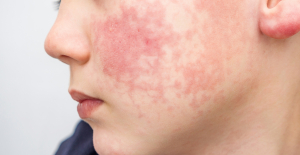 Parvovirus alert, the “fifth disease” of children which has already caused the death of five babies in 2024
Parvovirus alert, the “fifth disease” of children which has already caused the death of five babies in 2024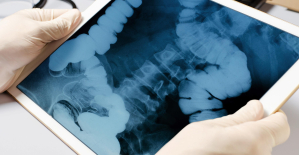 Colorectal cancer: what to watch out for in those under 50
Colorectal cancer: what to watch out for in those under 50 H5N1 virus: traces detected in pasteurized milk in the United States
H5N1 virus: traces detected in pasteurized milk in the United States Falling wings of the Moulin Rouge: who will pay for the repairs?
Falling wings of the Moulin Rouge: who will pay for the repairs? “You don’t sell a company like that”: Roland Lescure “annoyed” by the prospect of a sale of Biogaran
“You don’t sell a company like that”: Roland Lescure “annoyed” by the prospect of a sale of Biogaran Insults, threats of suicide, violence... Attacks by France Travail agents will continue to soar in 2023
Insults, threats of suicide, violence... Attacks by France Travail agents will continue to soar in 2023 TotalEnergies boss plans primary listing in New York
TotalEnergies boss plans primary listing in New York La Pléiade arrives... in Pléiade
La Pléiade arrives... in Pléiade In Japan, an animation studio bets on its creators suffering from autism spectrum disorders
In Japan, an animation studio bets on its creators suffering from autism spectrum disorders Terry Gilliam, hero of the Annecy Festival, with Vice-Versa 2 and Garfield
Terry Gilliam, hero of the Annecy Festival, with Vice-Versa 2 and Garfield François Hollande, Stéphane Bern and Amélie Nothomb, heroes of one evening on the beach of the Cannes Film Festival
François Hollande, Stéphane Bern and Amélie Nothomb, heroes of one evening on the beach of the Cannes Film Festival Skoda Kodiaq 2024: a 'beast' plug-in hybrid SUV
Skoda Kodiaq 2024: a 'beast' plug-in hybrid SUV Tesla launches a new Model Y with 600 km of autonomy at a "more accessible price"
Tesla launches a new Model Y with 600 km of autonomy at a "more accessible price" The 10 best-selling cars in March 2024 in Spain: sales fall due to Easter
The 10 best-selling cars in March 2024 in Spain: sales fall due to Easter A private jet company buys more than 100 flying cars
A private jet company buys more than 100 flying cars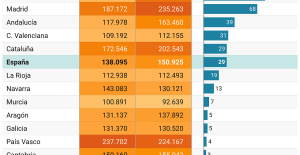 This is how housing prices have changed in Spain in the last decade
This is how housing prices have changed in Spain in the last decade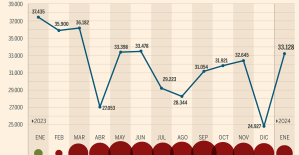 The home mortgage firm drops 10% in January and interest soars to 3.46%
The home mortgage firm drops 10% in January and interest soars to 3.46% The jewel of the Rocío de Nagüeles urbanization: a dream villa in Marbella
The jewel of the Rocío de Nagüeles urbanization: a dream villa in Marbella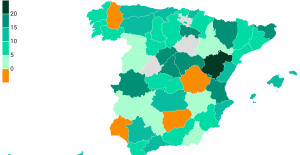 Rental prices grow by 7.3% in February: where does it go up and where does it go down?
Rental prices grow by 7.3% in February: where does it go up and where does it go down? Even on a mission for NATO, the Charles-de-Gaulle remains under French control, Lecornu responds to Mélenchon
Even on a mission for NATO, the Charles-de-Gaulle remains under French control, Lecornu responds to Mélenchon “Deadly Europe”, “economic decline”, immigration… What to remember from Emmanuel Macron’s speech at the Sorbonne
“Deadly Europe”, “economic decline”, immigration… What to remember from Emmanuel Macron’s speech at the Sorbonne Sale of Biogaran: The Republicans write to Emmanuel Macron
Sale of Biogaran: The Republicans write to Emmanuel Macron Europeans: “All those who claim that we don’t need Europe are liars”, criticizes Bayrou
Europeans: “All those who claim that we don’t need Europe are liars”, criticizes Bayrou These French cities that will boycott the World Cup in Qatar
These French cities that will boycott the World Cup in Qatar PSG: “We are in a splendid moment”, underlines Luis Enrique, who had “not even thought of such a positive scenario”
PSG: “We are in a splendid moment”, underlines Luis Enrique, who had “not even thought of such a positive scenario” Premier League: “I like the way his team plays football”, Klopp appreciates the work of his potential successor
Premier League: “I like the way his team plays football”, Klopp appreciates the work of his potential successor Top 14: “They don’t respect us, they spit on us,” thunders Urios (Clermont)
Top 14: “They don’t respect us, they spit on us,” thunders Urios (Clermont) “I am very happy to know that he continues at the club”: Luis Enrique spills the beans on Mayulu’s future at PSG
“I am very happy to know that he continues at the club”: Luis Enrique spills the beans on Mayulu’s future at PSG