A particularly aggressive fungal disease has decimated within 50 years, the stocks of more than 500 amphibian species around the globe. In 90 cases the species are already extinct in the wild, write researchers in a comprehensive investigation to the disease Chytridiomycosis in the journal "Science". Compiled by a Team led by Ben Scheele from the Australian National University in Canberra (Australia) has the data.
"The disease is caused by a chytrid fungus, which probably comes from Asia, where local amphibians appear to be resistant to the disease," Scheele cited in a communication from his University. Of the fungus of the frog, Duellmanohyla soralia, which is found in Honduras is affected, for example. Scheele makes the people for the spread of the fungus responsible: "globalization and the trade in wild animals are the main causes of this global pandemic and to enable the further spread of diseases."
especially species in Australia and Central and South America affected
From the Red lists of the literature and discussions with amphibian experts from around the world, the researchers have created an Overview of the effects of Chytridiomycosis. The disease is caused by Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis, a fungus that belongs to fungi of a group of otherwise harmless soil and Water. In one case, the fire Salamander (Salamandra salamandra) is the causative agent is a fungus of the same genus (Batrachochytrium salamandrivorans), which was only discovered in 2013.
from the disease Of Anurans and tail of amphibians in Central and South America and Australia are particularly affected. In the other parts of the world, the fungus is present, but only a few of the types of the disease.
fungal infection complicates the breathing through the skin
Overall, Chytridiomycosis is seen at 6.5 per cent of the scientifically described species of amphibians. From their data, the scientists have taken some risks: Population declines in species that have a large body, the life in constantly moist areas and are closely associated with aquatic habitats are connected.
The danger of the fungus has to do with several skills: He can infest many different types and uses types that are not by him ill, as a space of Survival. It can also be due to water transfer. The fungus attacks the skin of the animals, which is problematic for living organisms, in which the cutaneous respiration plays a very important role. Some species appear to develop resistance against the disease.
More aboutEndangered amphibians, The hardships of frog, newt and toad
Roland SchulzIn a commentary, also in Science, advocate Dan Greenberg and Wendy Palen of Simon Fraser University in Burnaby (Canada) to ensure that the findings should have consequences from the study: "It is extremely important that these data for proactive Management, which takes account of multiple threats." The loss of habitats and climate change were the main threats to thousands of species. You recommend to protect habitats, to restrict the Collecting of wild animals and trade of animals to contain. (dpa)

 After 13 years of mission and seven successive leaders, the UN at an impasse in Libya
After 13 years of mission and seven successive leaders, the UN at an impasse in Libya Germany: search of AfD headquarters in Lower Saxony, amid accusations of embezzlement
Germany: search of AfD headquarters in Lower Saxony, amid accusations of embezzlement Faced with Iran, Israel plays appeasement and continues its shadow war
Faced with Iran, Israel plays appeasement and continues its shadow war Iran-Israel conflict: what we know about the events of the night after the explosions in Isfahan
Iran-Israel conflict: what we know about the events of the night after the explosions in Isfahan Sánchez condemns Iran's attack on Israel and calls for "containment" to avoid an escalation
Sánchez condemns Iran's attack on Israel and calls for "containment" to avoid an escalation China's GDP grows 5.3% in the first quarter, more than expected
China's GDP grows 5.3% in the first quarter, more than expected Alert on the return of whooping cough, a dangerous respiratory infection for babies
Alert on the return of whooping cough, a dangerous respiratory infection for babies Can relaxation, sophrology and meditation help with insomnia?
Can relaxation, sophrology and meditation help with insomnia? Vacation departures and returns: with the first crossovers, heavy traffic is expected this weekend
Vacation departures and returns: with the first crossovers, heavy traffic is expected this weekend “Têtu”, “Ideat”, “The Good Life”… The magazines of the I/O Media group resold to several buyers
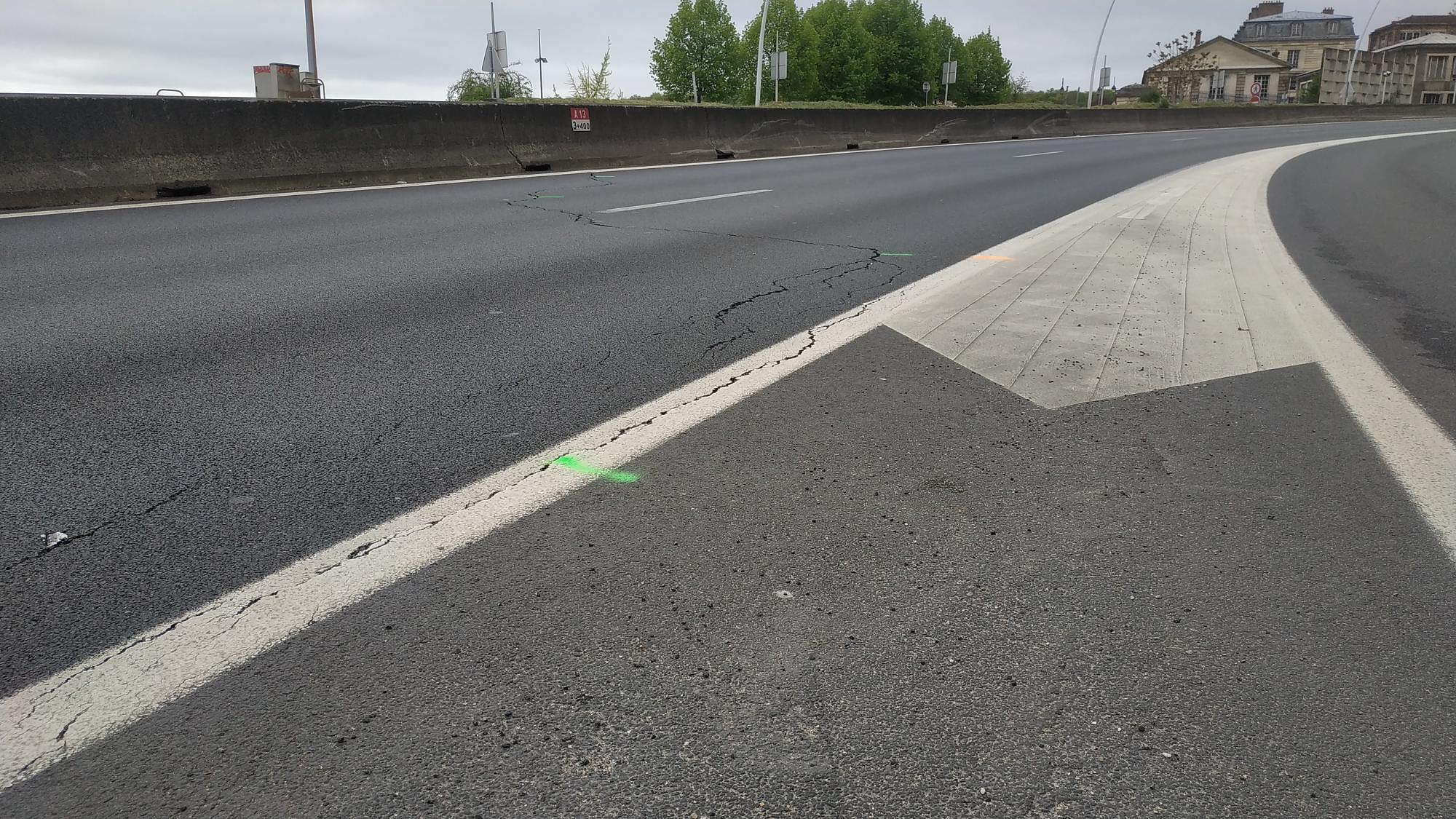
“Têtu”, “Ideat”, “The Good Life”… The magazines of the I/O Media group resold to several buyers The A13 motorway closed in both directions for an “indefinite period” between Paris and Normandy
The A13 motorway closed in both directions for an “indefinite period” between Paris and Normandy The commitment to reduce taxes of 2 billion euros for households “will be kept”, assures Gabriel Attal
The commitment to reduce taxes of 2 billion euros for households “will be kept”, assures Gabriel Attal The exclusive Vespa that pays tribute to 140 years of Piaggio
The exclusive Vespa that pays tribute to 140 years of Piaggio Kingdom of the great maxi scooters: few and Kymco wants the crown of the Yamaha TMax
Kingdom of the great maxi scooters: few and Kymco wants the crown of the Yamaha TMax A complaint filed against Kanye West, accused of hitting an individual who had just attacked his wife
A complaint filed against Kanye West, accused of hitting an individual who had just attacked his wife In Béarn, a call for donations to renovate the house of Henri IV's mother
In Béarn, a call for donations to renovate the house of Henri IV's mother Skoda Kodiaq 2024: a 'beast' plug-in hybrid SUV
Skoda Kodiaq 2024: a 'beast' plug-in hybrid SUV Tesla launches a new Model Y with 600 km of autonomy at a "more accessible price"
Tesla launches a new Model Y with 600 km of autonomy at a "more accessible price" The 10 best-selling cars in March 2024 in Spain: sales fall due to Easter
The 10 best-selling cars in March 2024 in Spain: sales fall due to Easter A private jet company buys more than 100 flying cars
A private jet company buys more than 100 flying cars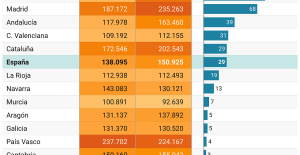 This is how housing prices have changed in Spain in the last decade
This is how housing prices have changed in Spain in the last decade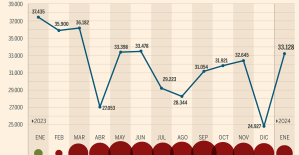 The home mortgage firm drops 10% in January and interest soars to 3.46%
The home mortgage firm drops 10% in January and interest soars to 3.46% The jewel of the Rocío de Nagüeles urbanization: a dream villa in Marbella
The jewel of the Rocío de Nagüeles urbanization: a dream villa in Marbella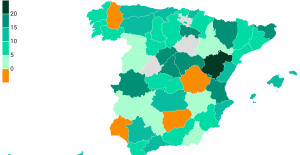 Rental prices grow by 7.3% in February: where does it go up and where does it go down?
Rental prices grow by 7.3% in February: where does it go up and where does it go down? With the promise of a “real burst of authority”, Gabriel Attal provokes the ire of the opposition
With the promise of a “real burst of authority”, Gabriel Attal provokes the ire of the opposition Europeans: the schedule of debates to follow between now and June 9
Europeans: the schedule of debates to follow between now and June 9 Europeans: “In France, there is a left and there is a right,” assures Bellamy
Europeans: “In France, there is a left and there is a right,” assures Bellamy During the night of the economy, the right points out the budgetary flaws of the macronie
During the night of the economy, the right points out the budgetary flaws of the macronie These French cities that will boycott the World Cup in Qatar
These French cities that will boycott the World Cup in Qatar Rally: Neuville and Evans neck and neck after the first day in Croatia
Rally: Neuville and Evans neck and neck after the first day in Croatia Gymnastics: after Rio and Tokyo, Frenchman Samir Aït Saïd qualified for the Paris 2024 Olympics
Gymnastics: after Rio and Tokyo, Frenchman Samir Aït Saïd qualified for the Paris 2024 Olympics Top 14: in the fight for maintenance, Perpignan has the wind at its back
Top 14: in the fight for maintenance, Perpignan has the wind at its back Top 14: Toulon-Toulouse, a necessarily special reunion for Melvyn Jaminet
Top 14: Toulon-Toulouse, a necessarily special reunion for Melvyn Jaminet


















