The "Columbia" was only 16 minutes away from landing. Millions of people around the world watched the cloudless blue sky over Texas on their TV in anticipation of the landing approach - but then the accident happened: the space shuttle broke up and burned up when it entered the earth's atmosphere, all seven crew members died. It was exactly 20 years ago on Wednesday.
In the control center in Florida, where at 8:59 a.m. local time the last unintelligible words from the "Columbia" were transmitted before the contact was lost, the faces of the astronauts' family members and the engineers were horrified. "Humanity is being led into darkness by the inspiration of discovery and the yearning for understanding," then-President George W. Bush said shortly afterwards to his country. "Our journey into space will continue."
Parts of the "Columbia" were later found scattered in a radius of 200 kilometers across Texas and the neighboring state of Louisiana - on freeways, in offices, in forests. A day that was supposed to be a triumph for the US space agency Nasa and manned space exploration ended in disaster. At a commemoration a few days ago, NASA commemorated the victims and everyone else who died while working on space travel.
The "Columbia" was not just any space shuttle. She was the first, the cornerstone of a fleet of national icons. On April 12, 1981, it lifted off from pad 39A at Kennedy Space Center, Florida. "STS-1", as the first mission was codenamed, was followed by four more space shuttles and more than 1300 days in space with 134 flights in a 30-year space shuttle era - until the "Atlantis" at the end of the mission "STS -135" in July 2011, coming from space for the last time, touched down on earth.
Something had already gone wrong at the start of the accidental mission "STS-107". As investigations later revealed, this made the disaster during the attempted landing inevitable. A piece of foam insulation from one of the shuttle's fuel tanks broke off, punching a hole in the leading edge of the left wing. NASA scientists noticed this, but underestimated the extent of the damage.
Some Nasa managers had concerns, a former Nasa engineer recently wrote in a guest article for the "York Daily Record". There was also a request for better photos of the damage, but this was rejected. An emergency rescue mission would likely have been possible, later investigations found. But NASA did nothing.
The piece of insulating foam had damaged the space shuttle's heat shield. When entering the earth's atmosphere, the instruments in the left wing failed one after the other due to overheating, the "Columbia" got out of control shortly before its planned 28th landing and finally broke up. According to studies, the seven astronauts - five Americans, including a woman, as well as the first Israeli in space and an Indian woman - had no chance to protect themselves. Rick Husband, William McCool, Michael Anderson, Kalpana Chawla, David Brown, Laurel Clark and Ilan Ramon were dead within seconds.
While the Columbia disaster wasn't the first in Shuttle history -- seven astronauts died when the Challenger broke up shortly after launch in 1986 -- it would change space travel forever. The space shuttle fleet was temporarily banished to the hangar for almost two years and extensive tests, investigations and improvements were ordered. The result was, among other things, better seats and seat belts.
In the meantime, the shuttles have been completely sorted out – and Nasa engineers have abandoned the idea of space shuttles, even if they can transport heavy cargo. Instead, the focus is on capsules, such as the "Crew Dragon" from Elon Musk's private space company SpaceX, which is already used to bring astronauts to the International Space Station (ISS). The Orion capsule, developed by NASA itself for the Artemis missions to the moon and later also to Mars, successfully completed its first real test flight at the end of 2022.
Because these pods are mounted on top of the rocket at launch, rather than next to it, they are less exposed to possible debris. In addition, in the event of an emergency, the astronauts could be freed from the capsule from above before or during launch. "We are working to never repeat our past mistakes," said NASA CEO Bill Nelson. dpa
"Aha! Ten minutes of everyday knowledge" is WELT's knowledge podcast. Every Tuesday and Thursday we answer everyday questions from the field of science. Subscribe to the podcast on Spotify, Apple Podcasts, Deezer, Amazon Music, among others, or directly via RSS feed.

 Germany: Man armed with machete enters university library and threatens staff
Germany: Man armed with machete enters university library and threatens staff His body naturally produces alcohol, he is acquitted after a drunk driving conviction
His body naturally produces alcohol, he is acquitted after a drunk driving conviction Who is David Pecker, the first key witness in Donald Trump's trial?
Who is David Pecker, the first key witness in Donald Trump's trial? What does the law on the expulsion of migrants to Rwanda adopted by the British Parliament contain?
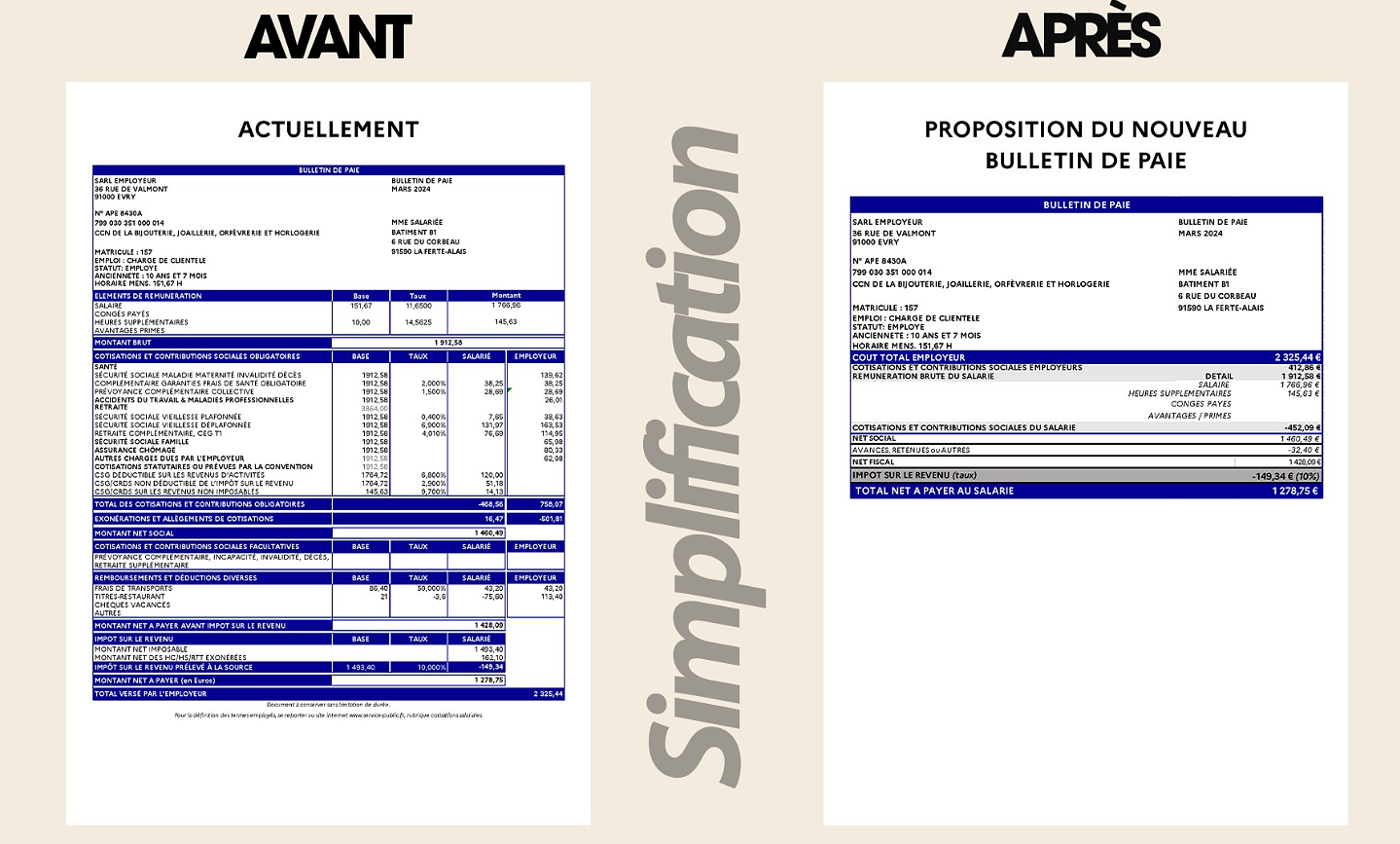
What does the law on the expulsion of migrants to Rwanda adopted by the British Parliament contain? Spain is the country in the European Union with the most overqualified workers for their jobs
Spain is the country in the European Union with the most overqualified workers for their jobs Parvovirus alert, the “fifth disease” of children which has already caused the death of five babies in 2024
Parvovirus alert, the “fifth disease” of children which has already caused the death of five babies in 2024 Colorectal cancer: what to watch out for in those under 50
Colorectal cancer: what to watch out for in those under 50 H5N1 virus: traces detected in pasteurized milk in the United States
H5N1 virus: traces detected in pasteurized milk in the United States Insurance: SFAM, subsidiary of Indexia, placed in compulsory liquidation
Insurance: SFAM, subsidiary of Indexia, placed in compulsory liquidation Under pressure from Brussels, TikTok deactivates the controversial mechanisms of its TikTok Lite application
Under pressure from Brussels, TikTok deactivates the controversial mechanisms of its TikTok Lite application “I can’t help but panic”: these passengers worried about incidents on Boeing
“I can’t help but panic”: these passengers worried about incidents on Boeing “I’m interested in knowing where the money that the State takes from me goes”: Bruno Le Maire’s strange pay slip sparks controversy
“I’m interested in knowing where the money that the State takes from me goes”: Bruno Le Maire’s strange pay slip sparks controversy 25 years later, the actors of Blair Witch Project are still demanding money to match the film's record profits
25 years later, the actors of Blair Witch Project are still demanding money to match the film's record profits At La Scala, Mathilde Charbonneaux is Madame M., Jacqueline Maillan
At La Scala, Mathilde Charbonneaux is Madame M., Jacqueline Maillan Deprived of Hollywood and Western music, Russia gives in to the charms of K-pop and manga
Deprived of Hollywood and Western music, Russia gives in to the charms of K-pop and manga Exhibition: Toni Grand, the incredible odyssey of a sculptural thinker
Exhibition: Toni Grand, the incredible odyssey of a sculptural thinker Skoda Kodiaq 2024: a 'beast' plug-in hybrid SUV
Skoda Kodiaq 2024: a 'beast' plug-in hybrid SUV Tesla launches a new Model Y with 600 km of autonomy at a "more accessible price"
Tesla launches a new Model Y with 600 km of autonomy at a "more accessible price" The 10 best-selling cars in March 2024 in Spain: sales fall due to Easter
The 10 best-selling cars in March 2024 in Spain: sales fall due to Easter A private jet company buys more than 100 flying cars
A private jet company buys more than 100 flying cars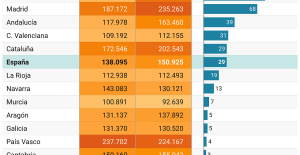 This is how housing prices have changed in Spain in the last decade
This is how housing prices have changed in Spain in the last decade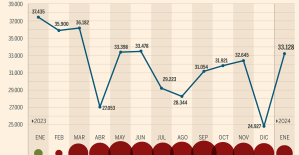 The home mortgage firm drops 10% in January and interest soars to 3.46%
The home mortgage firm drops 10% in January and interest soars to 3.46% The jewel of the Rocío de Nagüeles urbanization: a dream villa in Marbella
The jewel of the Rocío de Nagüeles urbanization: a dream villa in Marbella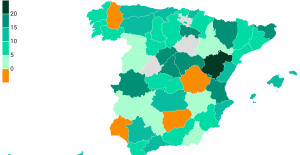 Rental prices grow by 7.3% in February: where does it go up and where does it go down?
Rental prices grow by 7.3% in February: where does it go up and where does it go down? Sale of Biogaran: The Republicans write to Emmanuel Macron
Sale of Biogaran: The Republicans write to Emmanuel Macron Europeans: “All those who claim that we don’t need Europe are liars”, criticizes Bayrou
Europeans: “All those who claim that we don’t need Europe are liars”, criticizes Bayrou With the promise of a “real burst of authority”, Gabriel Attal provokes the ire of the opposition
With the promise of a “real burst of authority”, Gabriel Attal provokes the ire of the opposition Europeans: the schedule of debates to follow between now and June 9
Europeans: the schedule of debates to follow between now and June 9 These French cities that will boycott the World Cup in Qatar
These French cities that will boycott the World Cup in Qatar Hand: Montpellier crushes Kiel and continues to dream of the Champions League
Hand: Montpellier crushes Kiel and continues to dream of the Champions League OM-Nice: a spectacular derby, Niçois timid despite their numerical superiority...The tops and the flops
OM-Nice: a spectacular derby, Niçois timid despite their numerical superiority...The tops and the flops Tennis: 1000 matches and 10 notable encounters by Richard Gasquet
Tennis: 1000 matches and 10 notable encounters by Richard Gasquet Tennis: first victory of the season on clay for Osaka in Madrid
Tennis: first victory of the season on clay for Osaka in Madrid