This sanction comes in a context of increased fines and legal proceedings in the EU and the United States against technology behemoths such as Google, Amazon, Facebook and Apple, the famous "GAFA".
"The Data Protection Commission (DPC) announces (...) the conclusion of an investigation into Meta Platforms Ireland Limited", a subsidiary of Meta and "body which controls the data of the social network Facebook, imposing a fine of 265 million euros and a series of corrective measures," wrote the DPC on Monday in a press release.
The Irish policeman announced in April 2021 the opening of an investigation targeting Facebook on behalf of the EU, after the revelation of a hacking by hackers of the data of more than 530 million users dating back to 2019.
The investigation focused on the applications "Facebook Search, Facebook Messenger Contact Importer and Instagram Contact Importer (...) between May 25, 2018 and September 2019", and sought to know if Meta had protected the data of its users sufficiently at the with regard to European regulations, the GDPR.
Facebook's European headquarters are in Ireland, like many Silicon Valley giants, and so it falls to the Irish regulator to investigate them on behalf of the European Union (EU).
The decision to impose a fine on Meta and its subsidiaries concerned was taken on Friday following findings of "breaches of European regulations (GDPR)", details the DPC.
- Looting of profiles -
The hack used a method known as "scraping" Facebook profiles via software that mimics the network's functionality that helps members easily find friends, scraping contact lists.
"Protecting people's personal data is critical to how our business operates," a Meta spokesperson said. "That's why we have fully cooperated with the Data Protection Commission on this important issue. We have made changes to our systems," he added.
GDPR, launched in 2018, gives regulators more power to protect consumers from the dominance of Facebook, Google, Apple and Twitter and others who, lured by favorable taxation, have chosen Ireland as their home base in Europe.
Regulators can impose a fine of up to 4% of the global turnover of these groups.
In the case of Facebook, the hacked data in question had been partly published on a hacker forum after being obtained by "malicious actors", Facebook explained.
The European Union, certain member countries, but also the United States, have multiplied in recent years the disputes with the digital giants on the protection of personal data but also taxation or abuse of a dominant position, among others.
In July 2019, Facebook was fined a record $5 billion by US federal authorities for "misleading" its users about their ability to control the privacy of their personal information, following the Cambridge Analytica scandal.
In France, the Cnil, guarantor of privacy on the internet, sentenced Facebook in January 2022 to a fine of 60 million euros for its practices in terms of "cookies", these digital tracers used to better target advertising.
After being criticized for its inaction, the DPC in March imposed a fine of 17 million euros for a series of twelve data breach notifications that occurred in 2018, then in September a sanction of 405 million euros for shortcomings in the processing of minors' data.
In September 2021, the DPC also sanctioned Whatsapp (Meta's instant messaging service) with a fine of 225 million euros for failing to meet its transparency obligations on data transfers with the group's other products.
Meta shares fell 0.91% to 110.14 dollars on the Nasdaq at 3:20 p.m. GMT.

 After 13 years of mission and seven successive leaders, the UN at an impasse in Libya
After 13 years of mission and seven successive leaders, the UN at an impasse in Libya Germany: search of AfD headquarters in Lower Saxony, amid accusations of embezzlement
Germany: search of AfD headquarters in Lower Saxony, amid accusations of embezzlement Faced with Iran, Israel plays appeasement and continues its shadow war
Faced with Iran, Israel plays appeasement and continues its shadow war Iran-Israel conflict: what we know about the events of the night after the explosions in Isfahan
Iran-Israel conflict: what we know about the events of the night after the explosions in Isfahan Sánchez condemns Iran's attack on Israel and calls for "containment" to avoid an escalation
Sánchez condemns Iran's attack on Israel and calls for "containment" to avoid an escalation China's GDP grows 5.3% in the first quarter, more than expected
China's GDP grows 5.3% in the first quarter, more than expected Alert on the return of whooping cough, a dangerous respiratory infection for babies
Alert on the return of whooping cough, a dangerous respiratory infection for babies Can relaxation, sophrology and meditation help with insomnia?
Can relaxation, sophrology and meditation help with insomnia? Vacation departures and returns: with the first crossovers, heavy traffic is expected this weekend
Vacation departures and returns: with the first crossovers, heavy traffic is expected this weekend “Têtu”, “Ideat”, “The Good Life”… The magazines of the I/O Media group resold to several buyers
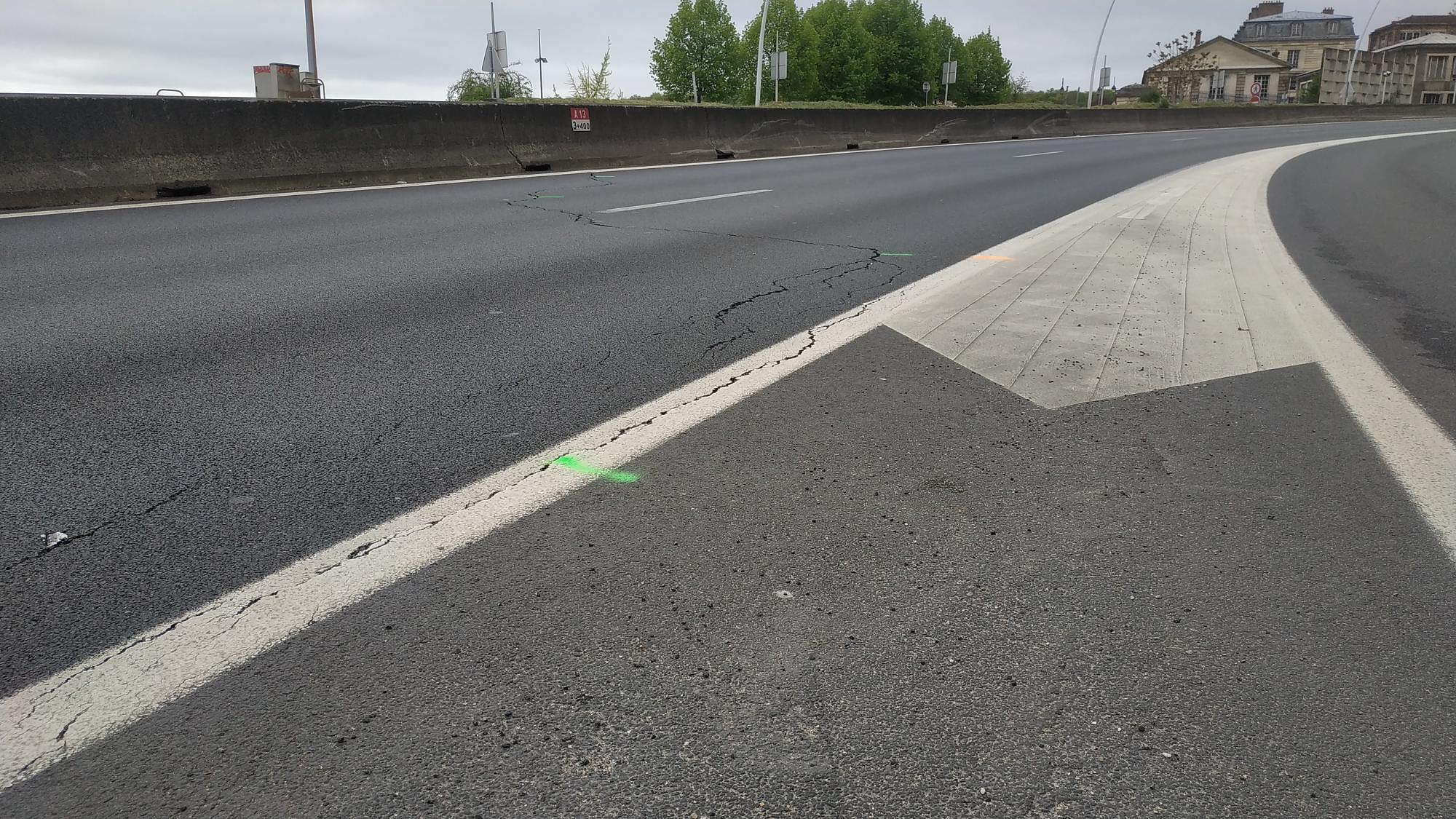
“Têtu”, “Ideat”, “The Good Life”… The magazines of the I/O Media group resold to several buyers The A13 motorway closed in both directions for an “indefinite period” between Paris and Normandy
The A13 motorway closed in both directions for an “indefinite period” between Paris and Normandy The commitment to reduce taxes of 2 billion euros for households “will be kept”, assures Gabriel Attal
The commitment to reduce taxes of 2 billion euros for households “will be kept”, assures Gabriel Attal The exclusive Vespa that pays tribute to 140 years of Piaggio
The exclusive Vespa that pays tribute to 140 years of Piaggio Kingdom of the great maxi scooters: few and Kymco wants the crown of the Yamaha TMax
Kingdom of the great maxi scooters: few and Kymco wants the crown of the Yamaha TMax A complaint filed against Kanye West, accused of hitting an individual who had just attacked his wife
A complaint filed against Kanye West, accused of hitting an individual who had just attacked his wife In Béarn, a call for donations to renovate the house of Henri IV's mother
In Béarn, a call for donations to renovate the house of Henri IV's mother Skoda Kodiaq 2024: a 'beast' plug-in hybrid SUV
Skoda Kodiaq 2024: a 'beast' plug-in hybrid SUV Tesla launches a new Model Y with 600 km of autonomy at a "more accessible price"
Tesla launches a new Model Y with 600 km of autonomy at a "more accessible price" The 10 best-selling cars in March 2024 in Spain: sales fall due to Easter
The 10 best-selling cars in March 2024 in Spain: sales fall due to Easter A private jet company buys more than 100 flying cars
A private jet company buys more than 100 flying cars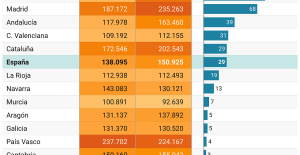 This is how housing prices have changed in Spain in the last decade
This is how housing prices have changed in Spain in the last decade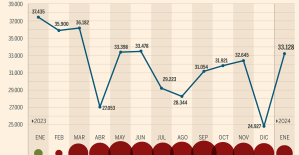 The home mortgage firm drops 10% in January and interest soars to 3.46%
The home mortgage firm drops 10% in January and interest soars to 3.46% The jewel of the Rocío de Nagüeles urbanization: a dream villa in Marbella
The jewel of the Rocío de Nagüeles urbanization: a dream villa in Marbella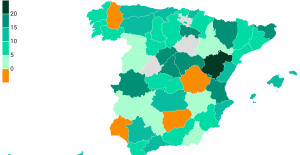 Rental prices grow by 7.3% in February: where does it go up and where does it go down?
Rental prices grow by 7.3% in February: where does it go up and where does it go down? With the promise of a “real burst of authority”, Gabriel Attal provokes the ire of the opposition
With the promise of a “real burst of authority”, Gabriel Attal provokes the ire of the opposition Europeans: the schedule of debates to follow between now and June 9
Europeans: the schedule of debates to follow between now and June 9 Europeans: “In France, there is a left and there is a right,” assures Bellamy
Europeans: “In France, there is a left and there is a right,” assures Bellamy During the night of the economy, the right points out the budgetary flaws of the macronie
During the night of the economy, the right points out the budgetary flaws of the macronie These French cities that will boycott the World Cup in Qatar
These French cities that will boycott the World Cup in Qatar Women's C1: at what time and on which channel to watch the OL-PSG semi-final first leg
Women's C1: at what time and on which channel to watch the OL-PSG semi-final first leg Tennis: after two victories this Friday, Grégoire Barrère qualifies for the semi-finals of the Bucharest tournament
Tennis: after two victories this Friday, Grégoire Barrère qualifies for the semi-finals of the Bucharest tournament Cycling: Mathieu Van der Poel “recharged the batteries” for Liège-Bastogne-Liège
Cycling: Mathieu Van der Poel “recharged the batteries” for Liège-Bastogne-Liège Mercato: Zidane at Bayern? We'll talk about it again, but...
Mercato: Zidane at Bayern? We'll talk about it again, but...


















